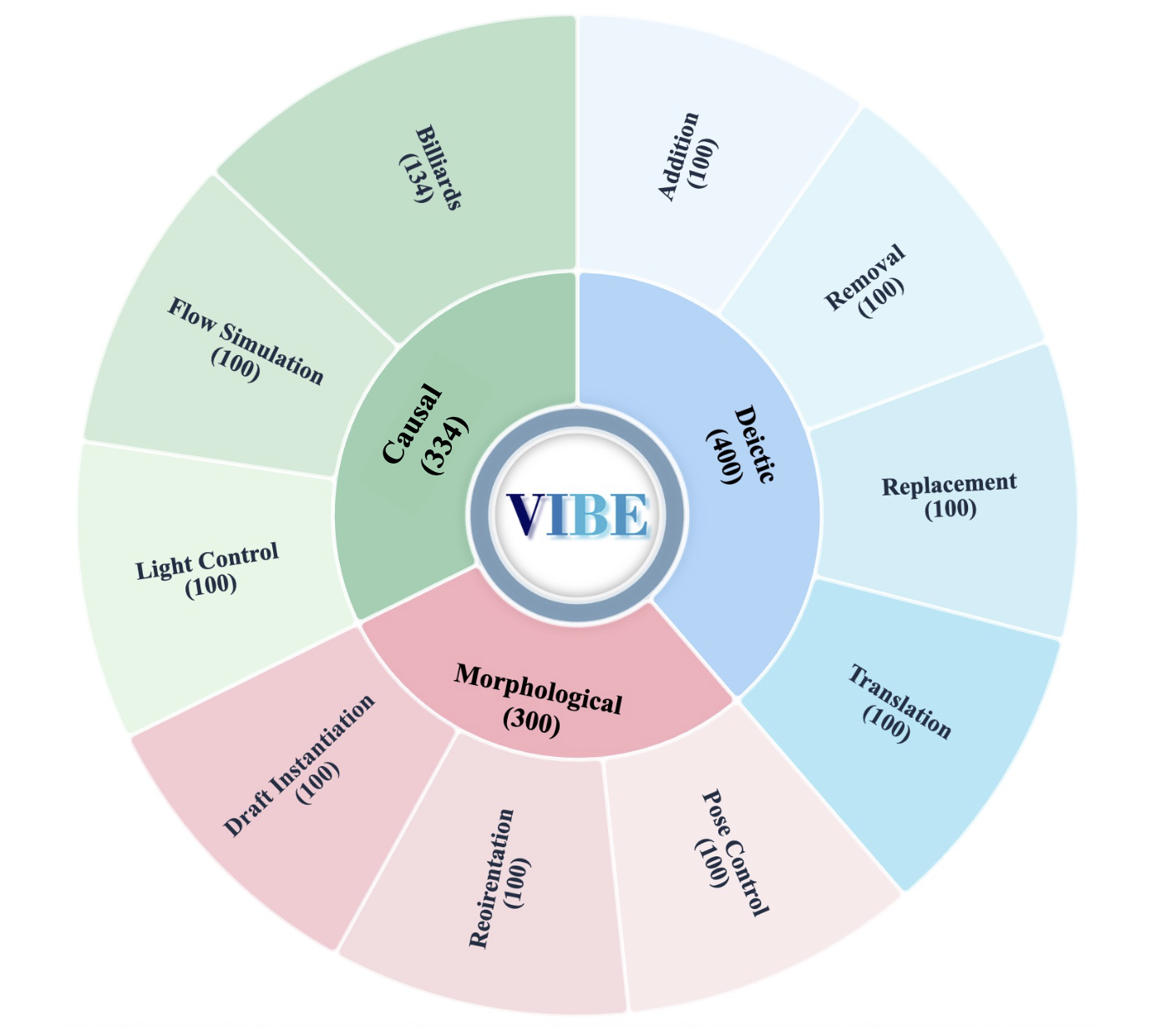
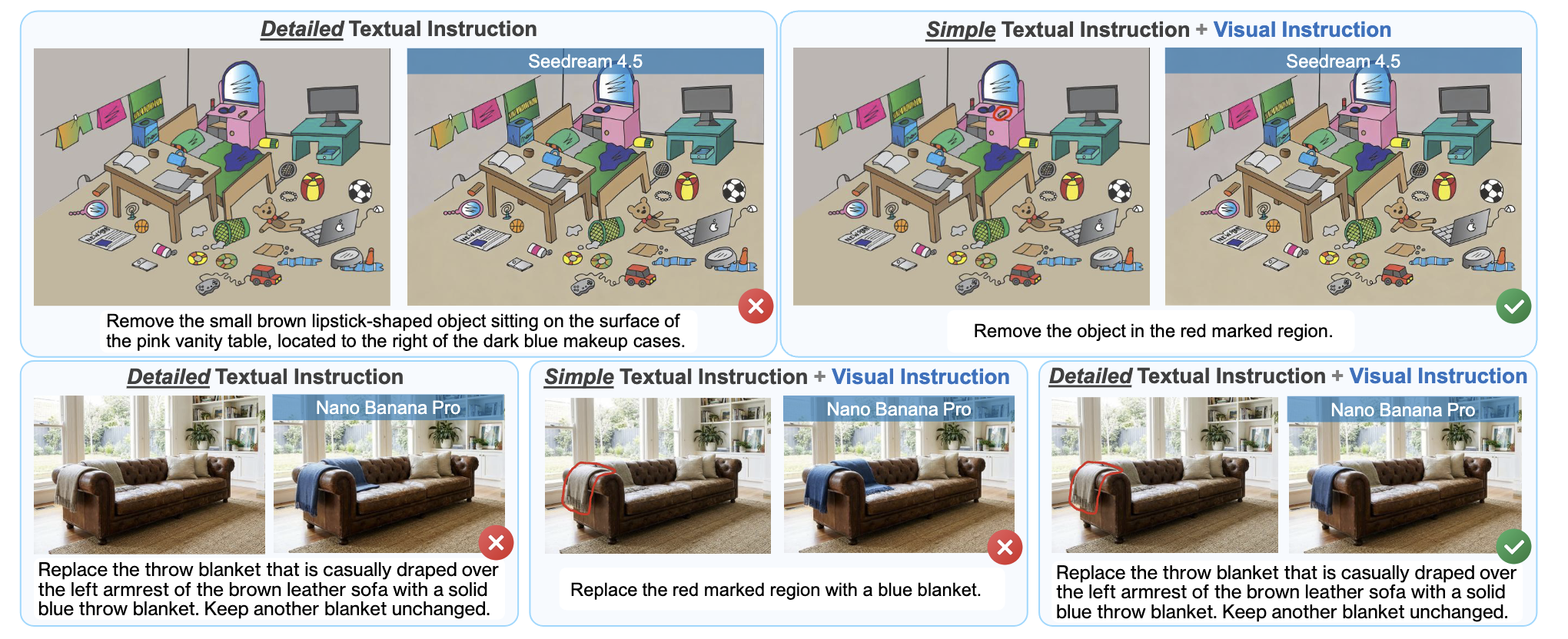
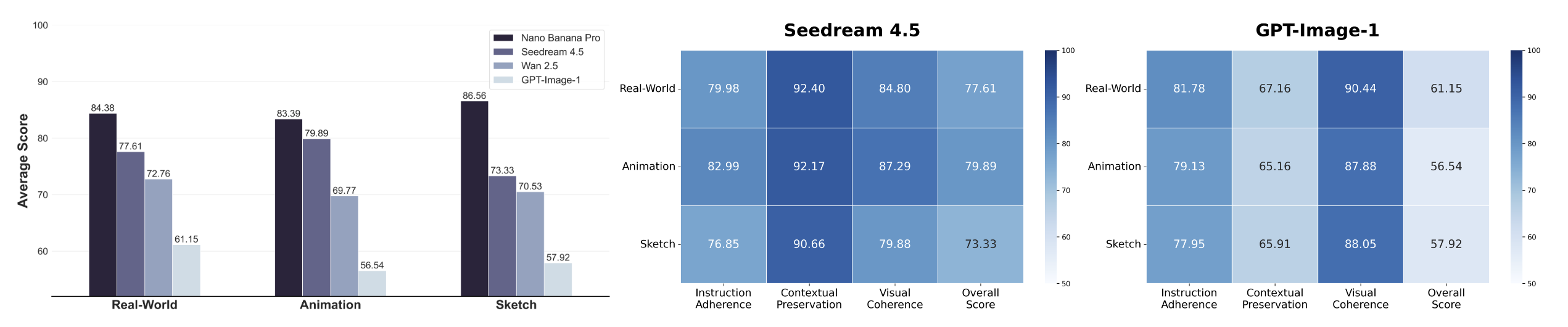
Visual Instruction-Driven Image Editing
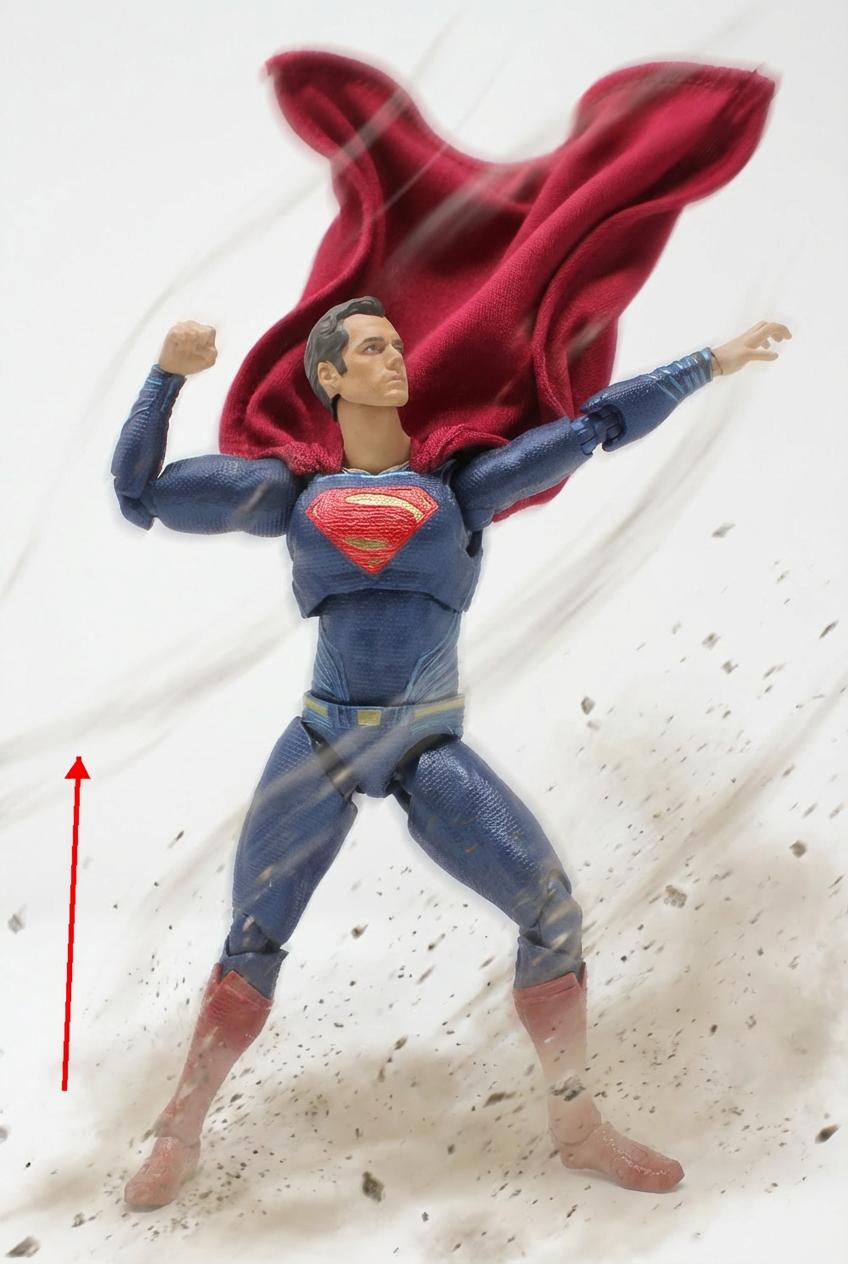
 Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
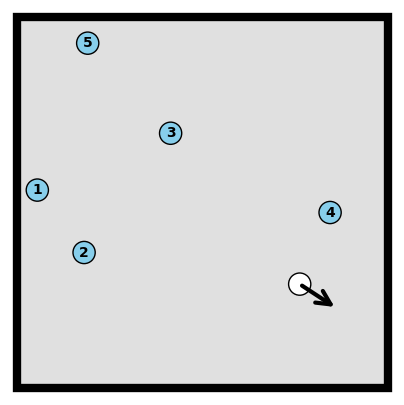
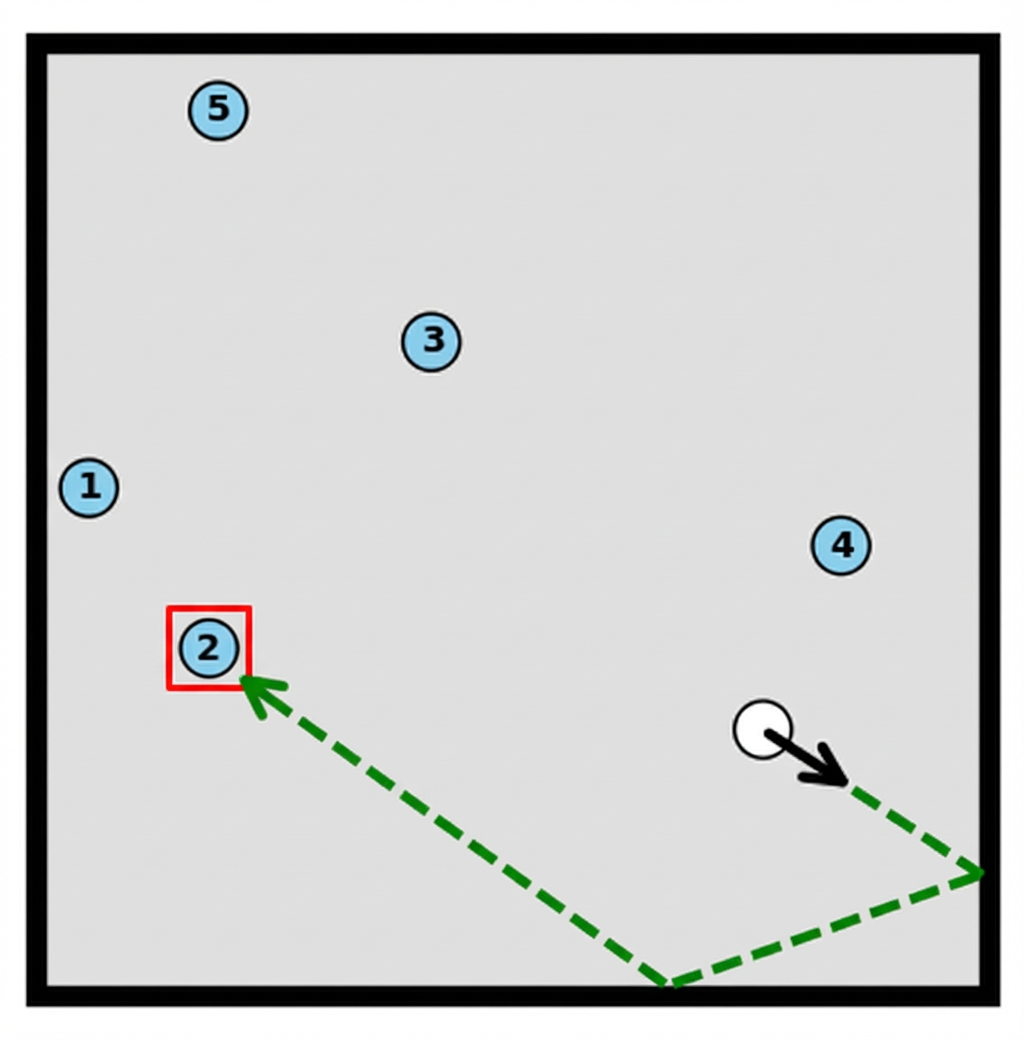 Add a green dashed line trajectory to the image, starting from the white ball and moving in the direction of the black arrow. Draw a red bounding box around the first blue ball that is hit by the trajectory.
Nano Banana Pro
Add a green dashed line trajectory to the image, starting from the white ball and moving in the direction of the black arrow. Draw a red bounding box around the first blue ball that is hit by the trajectory.
Nano Banana Pro
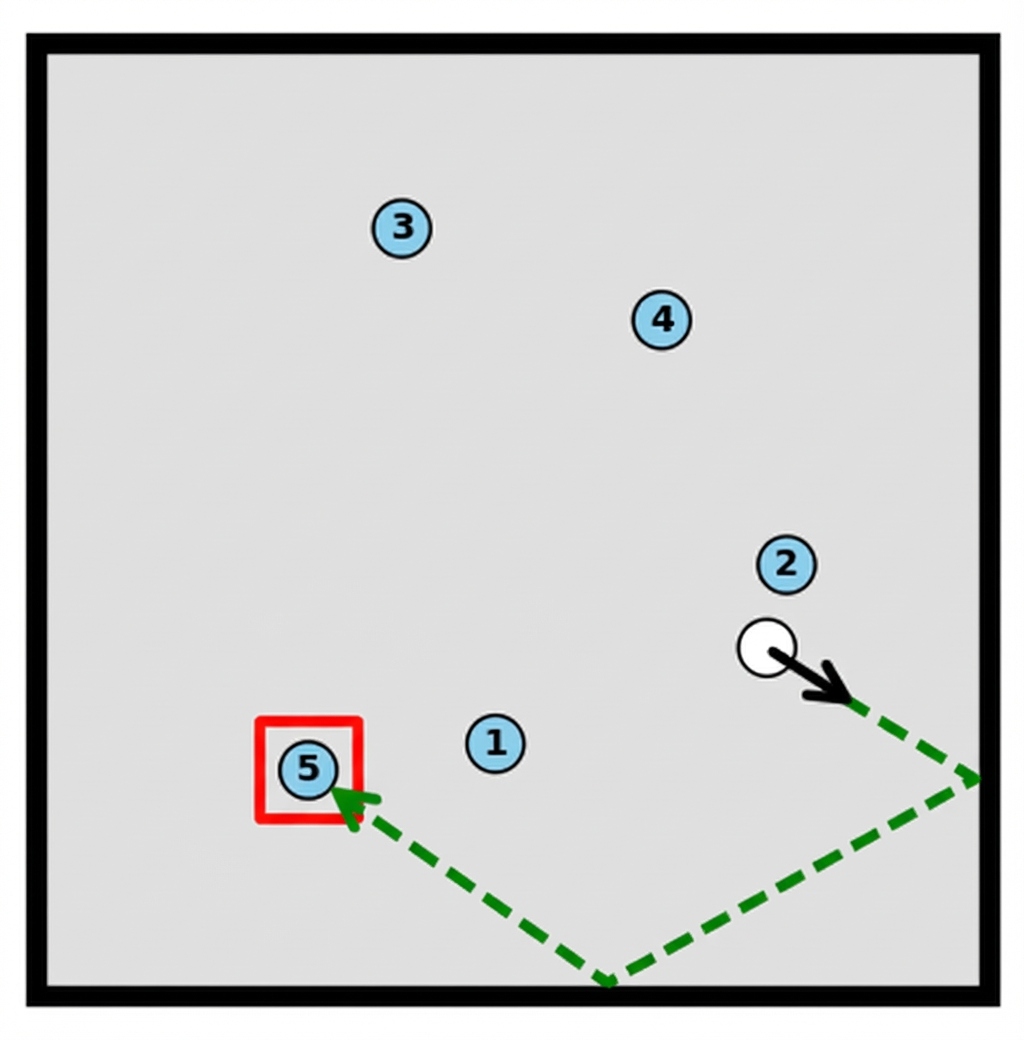 Add a green dashed line trajectory to the image, starting from the white ball and moving in the direction of the black arrow. Draw a red bounding box around the first blue ball that is hit by the trajectory.
Nano Banana Pro
Add a green dashed line trajectory to the image, starting from the white ball and moving in the direction of the black arrow. Draw a red bounding box around the first blue ball that is hit by the trajectory.
Nano Banana Pro
 Relocate the pencil highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Relocate the pencil highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
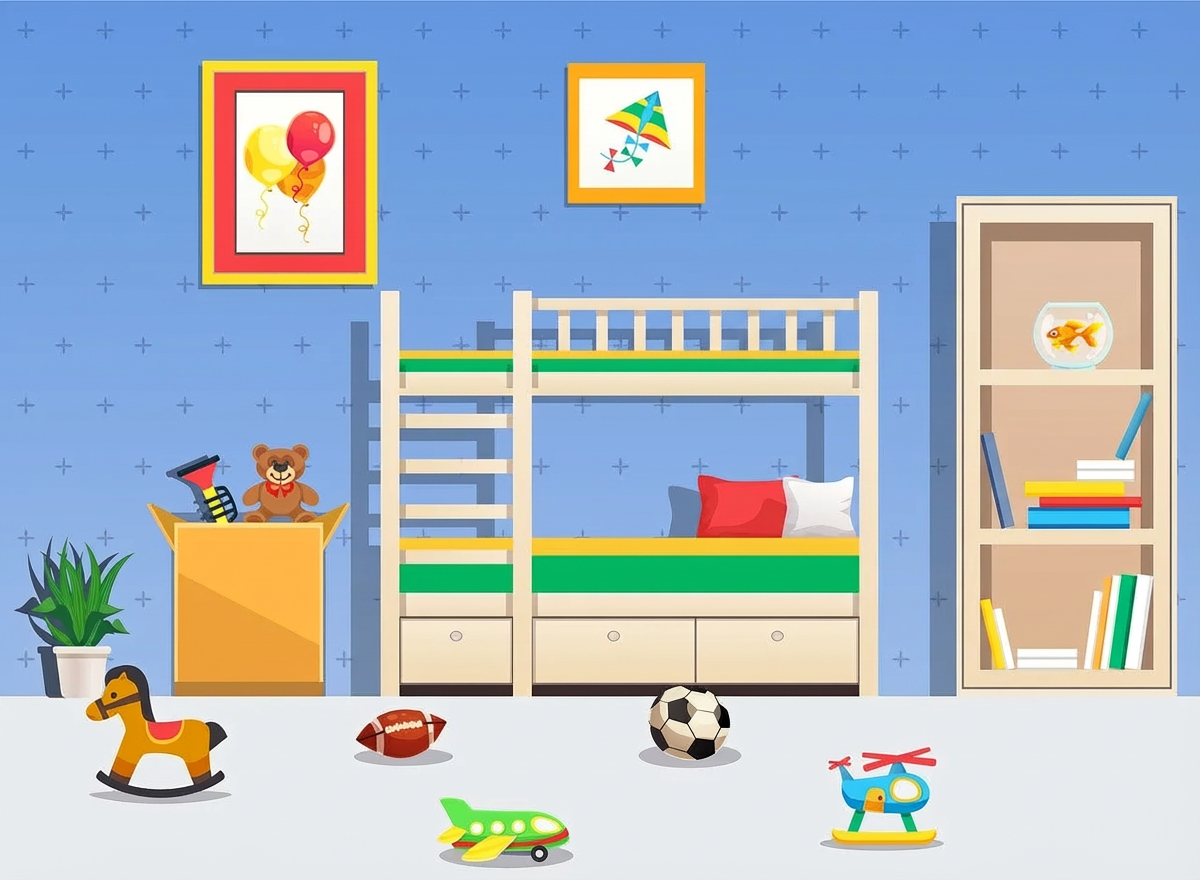
 Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
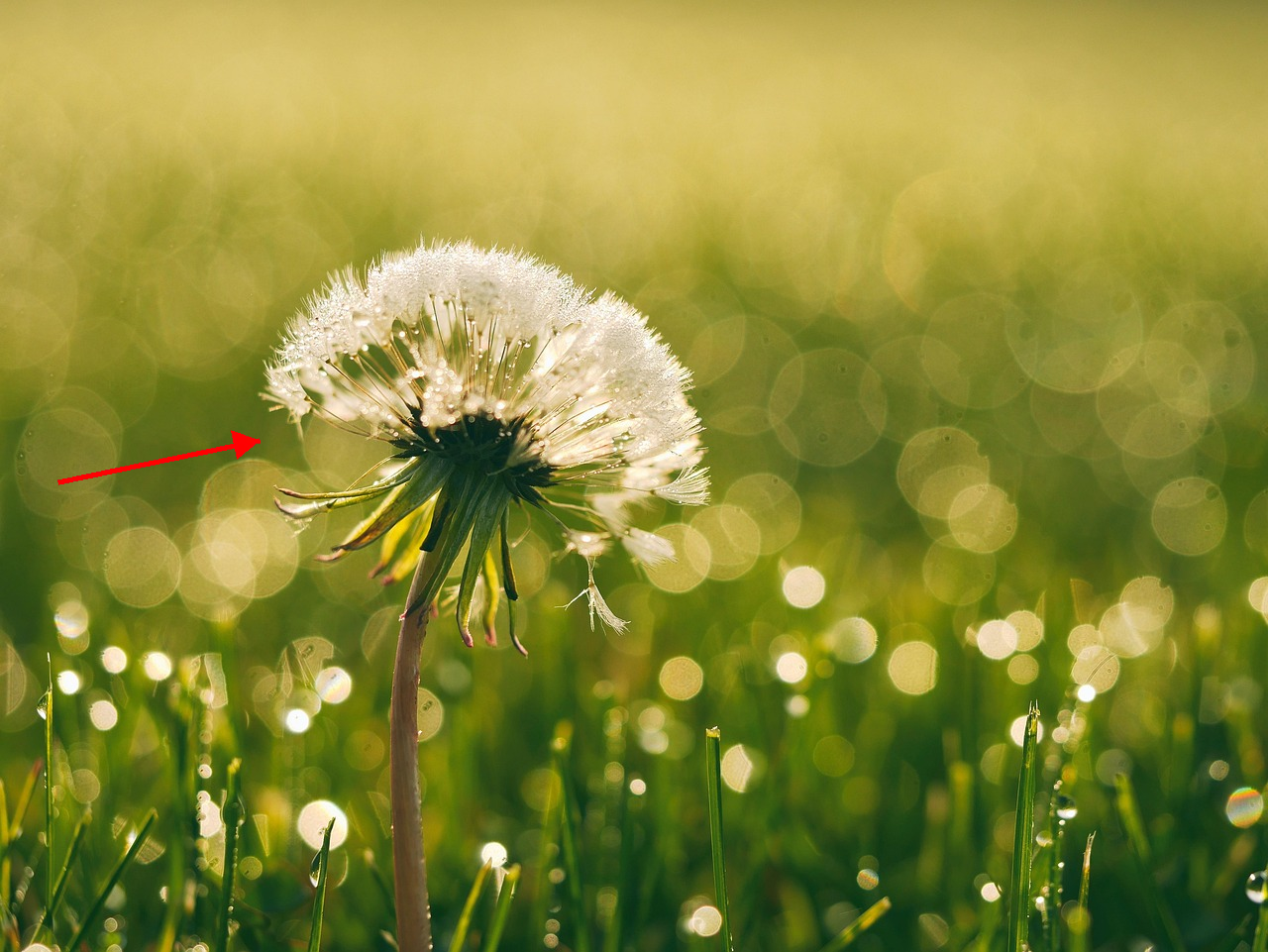
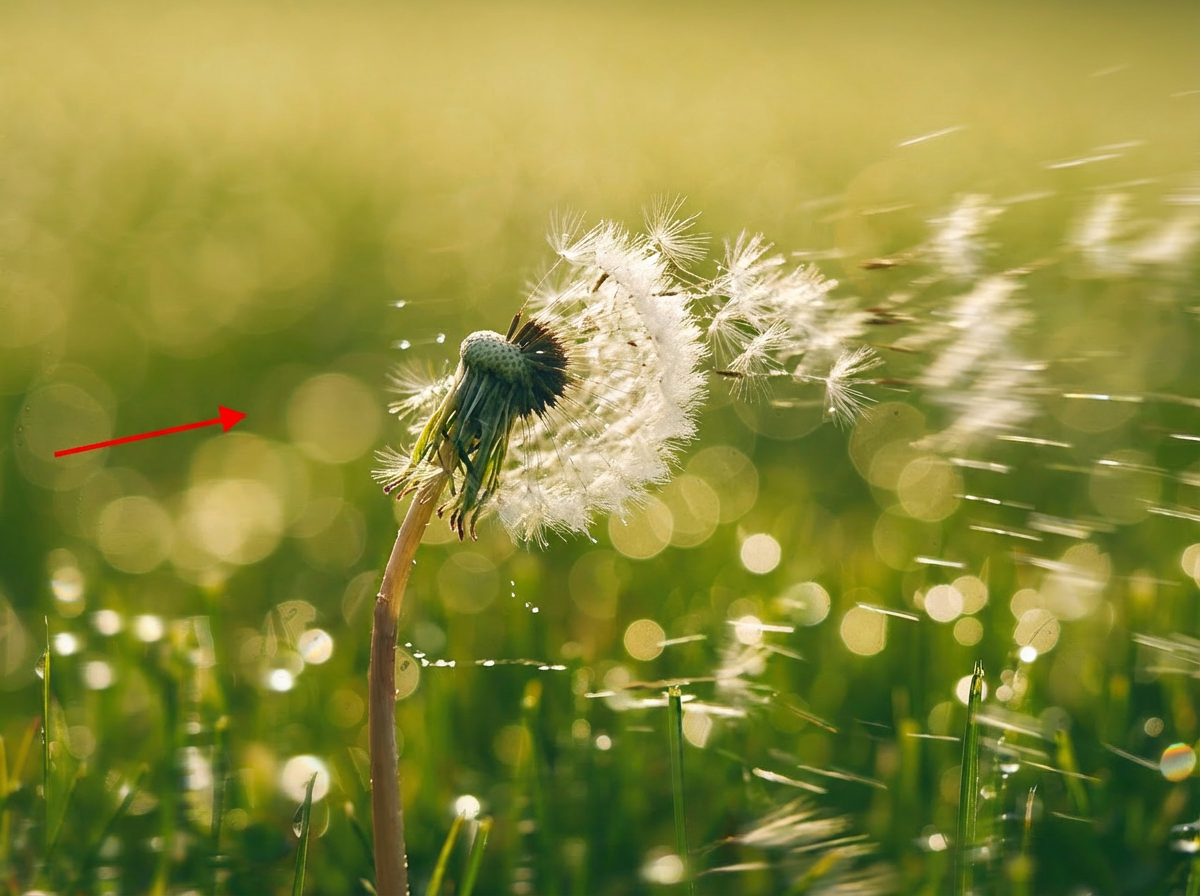
 Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
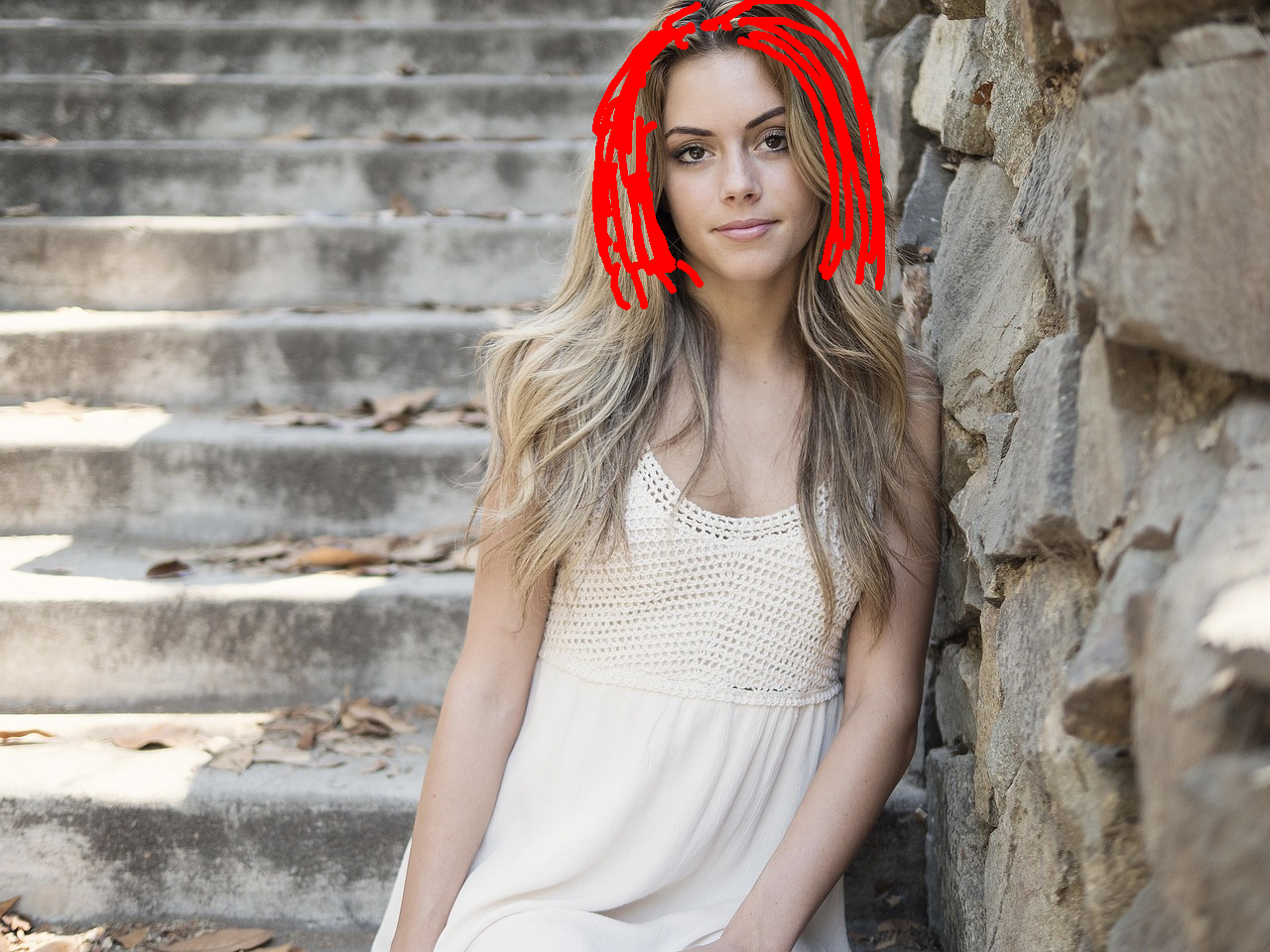
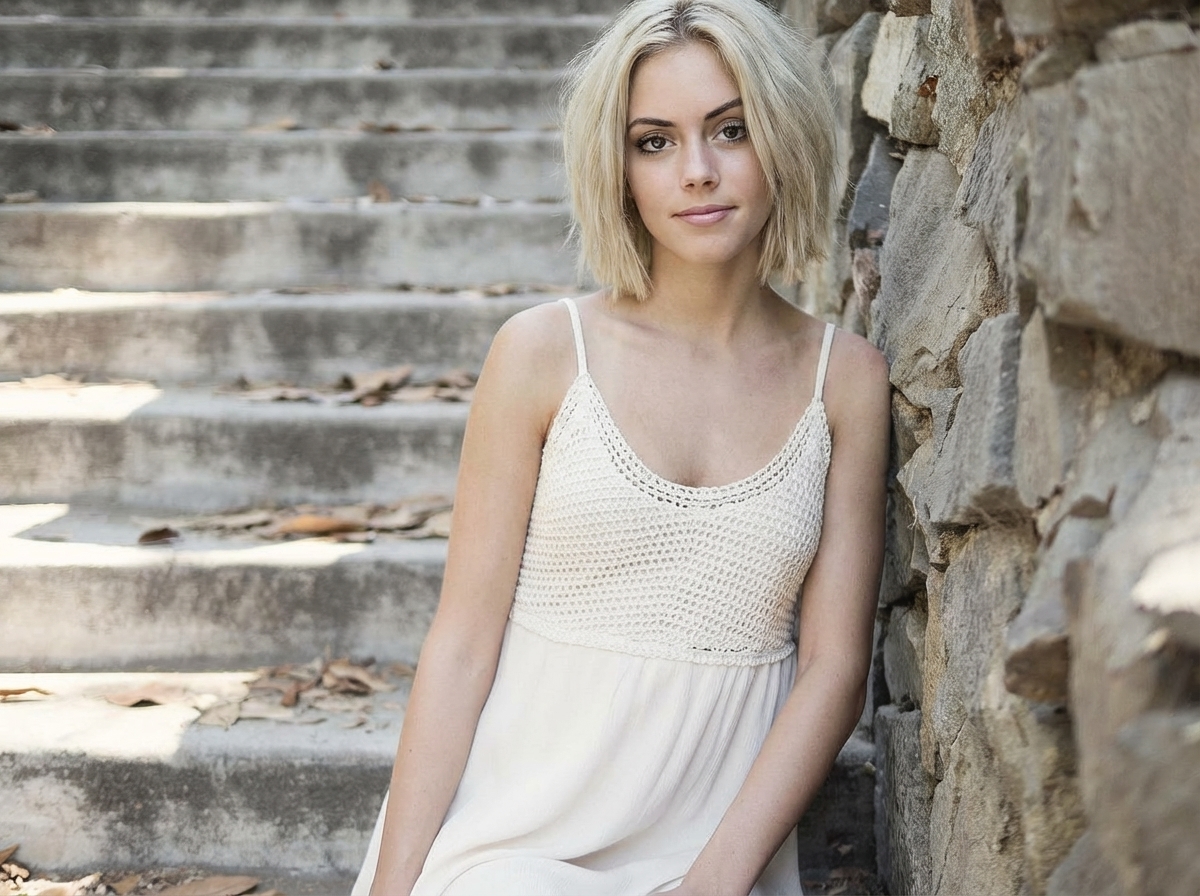
 Based on the red sketch annotations in the image, make this woman's hair short.
Nano Banana Pro
Based on the red sketch annotations in the image, make this woman's hair short.
Nano Banana Pro
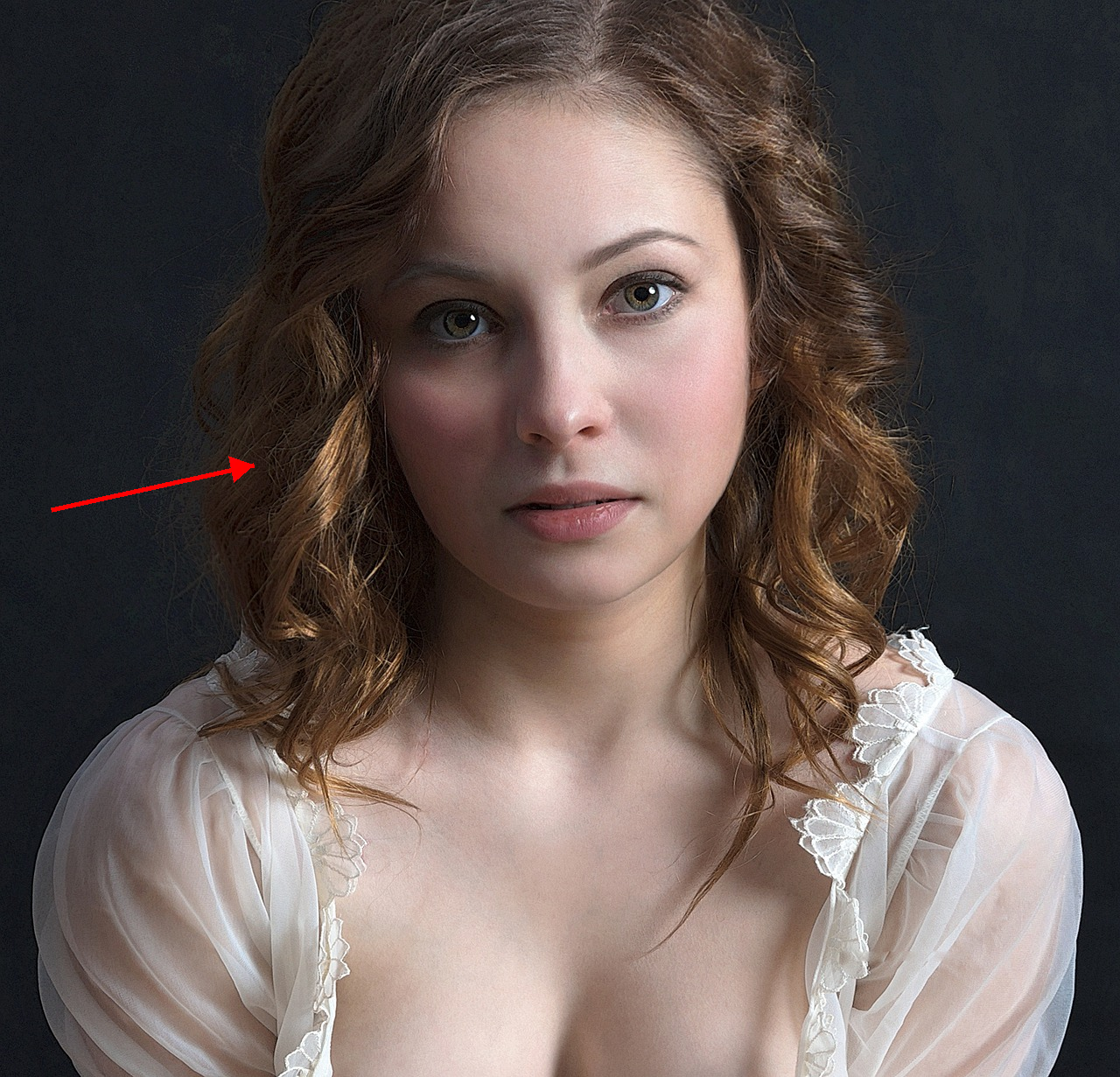
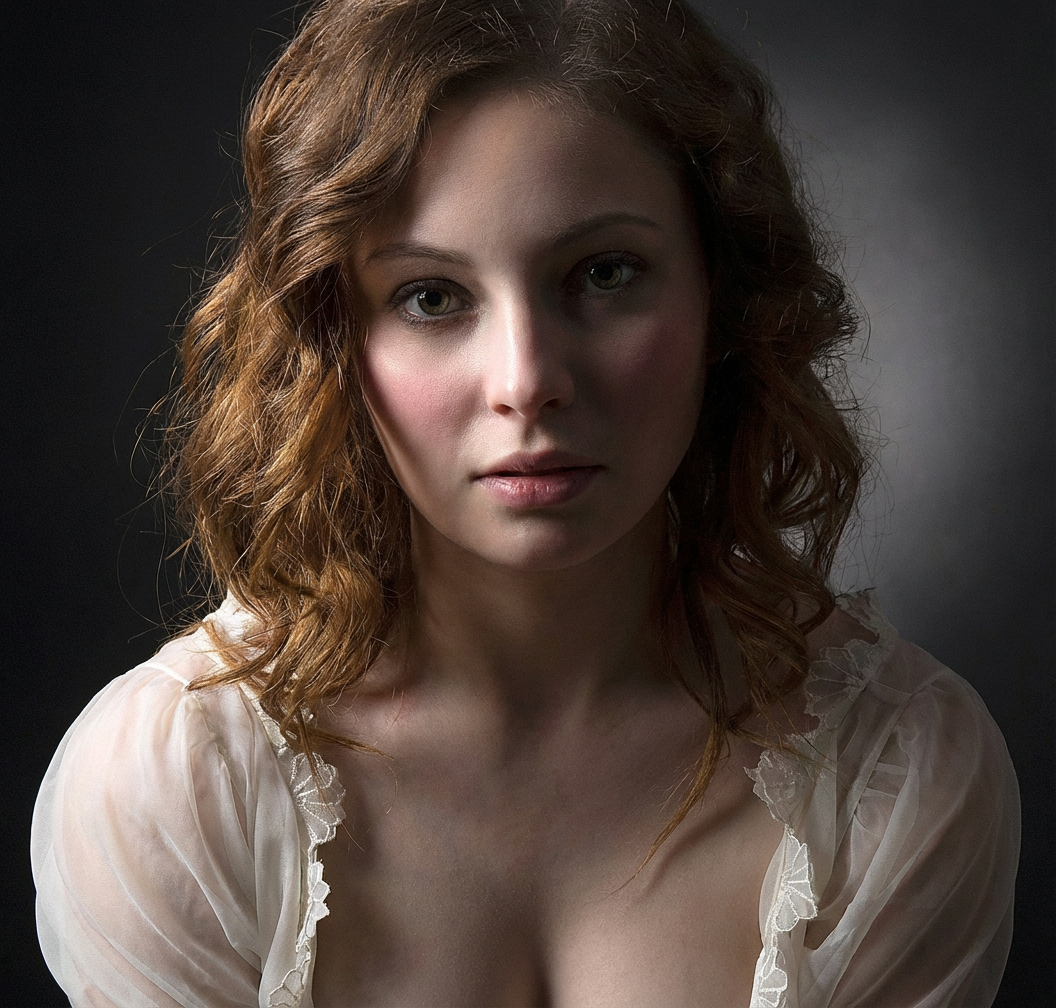
 Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
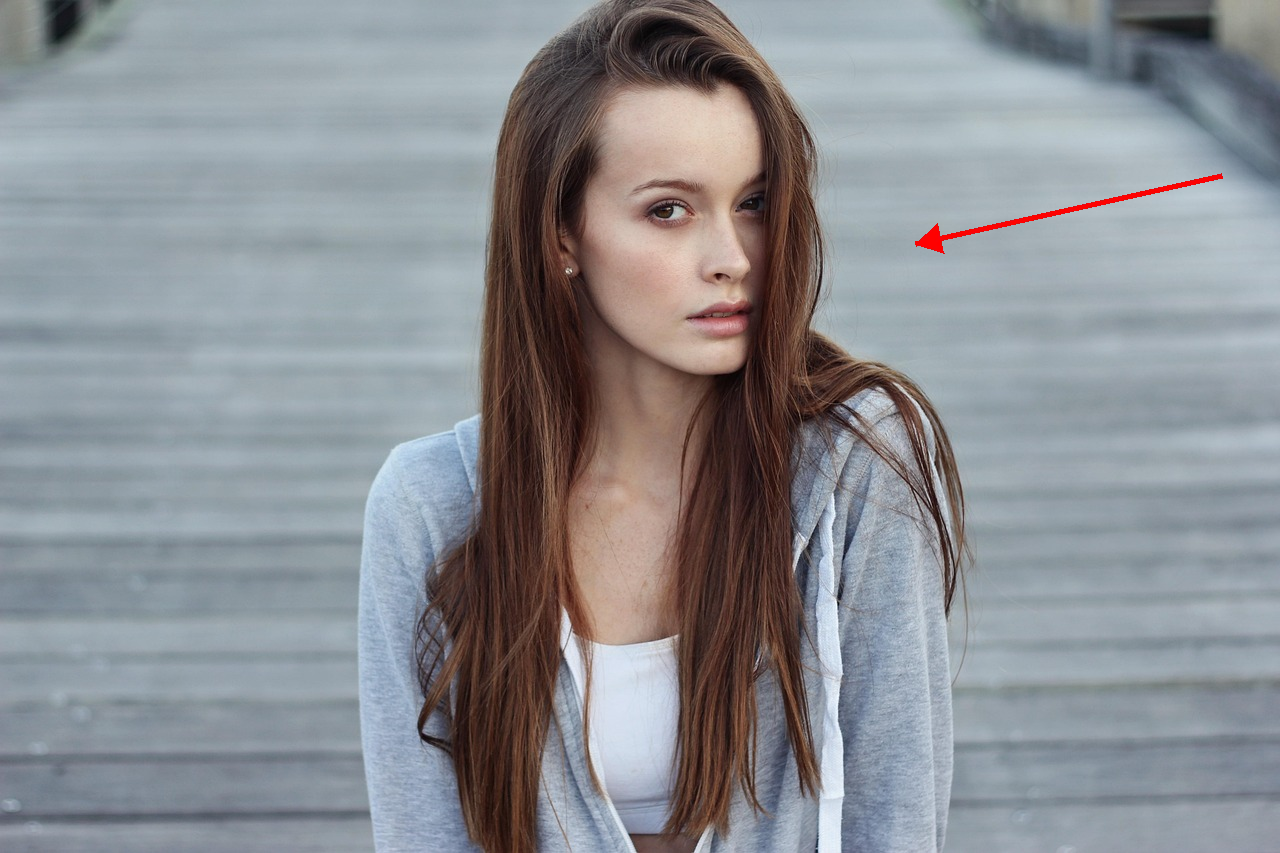
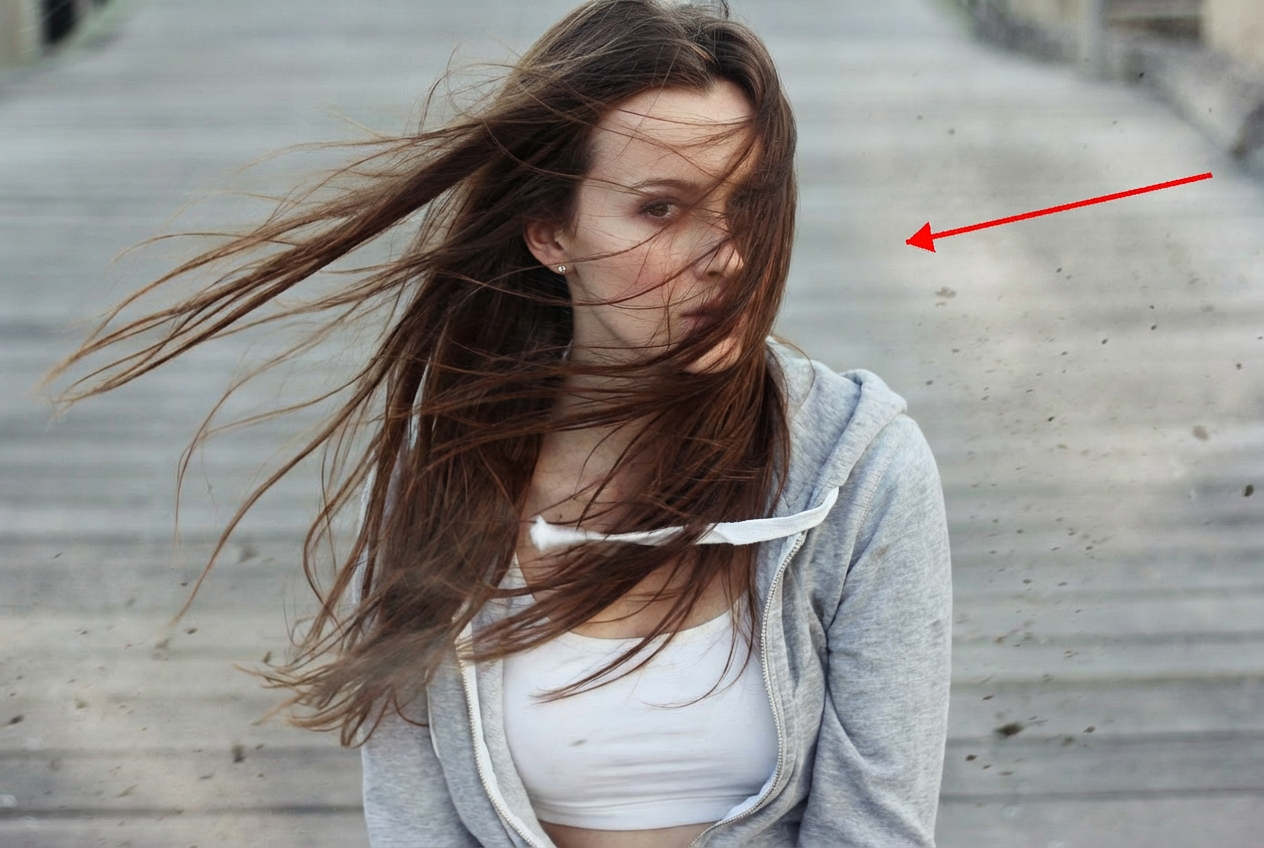
 Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Apply a wind effect to the entire scene. The wind direction must align precisely with the vector indicated by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
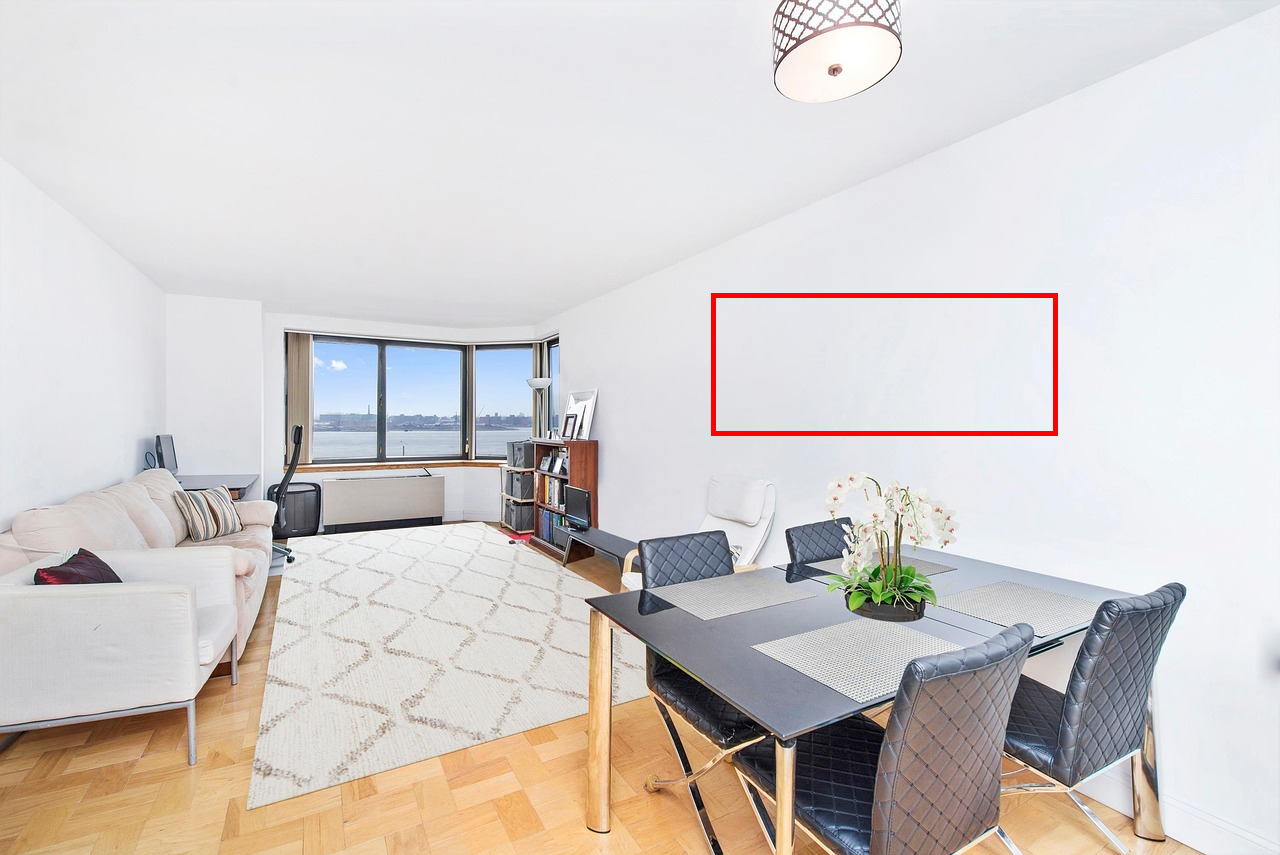
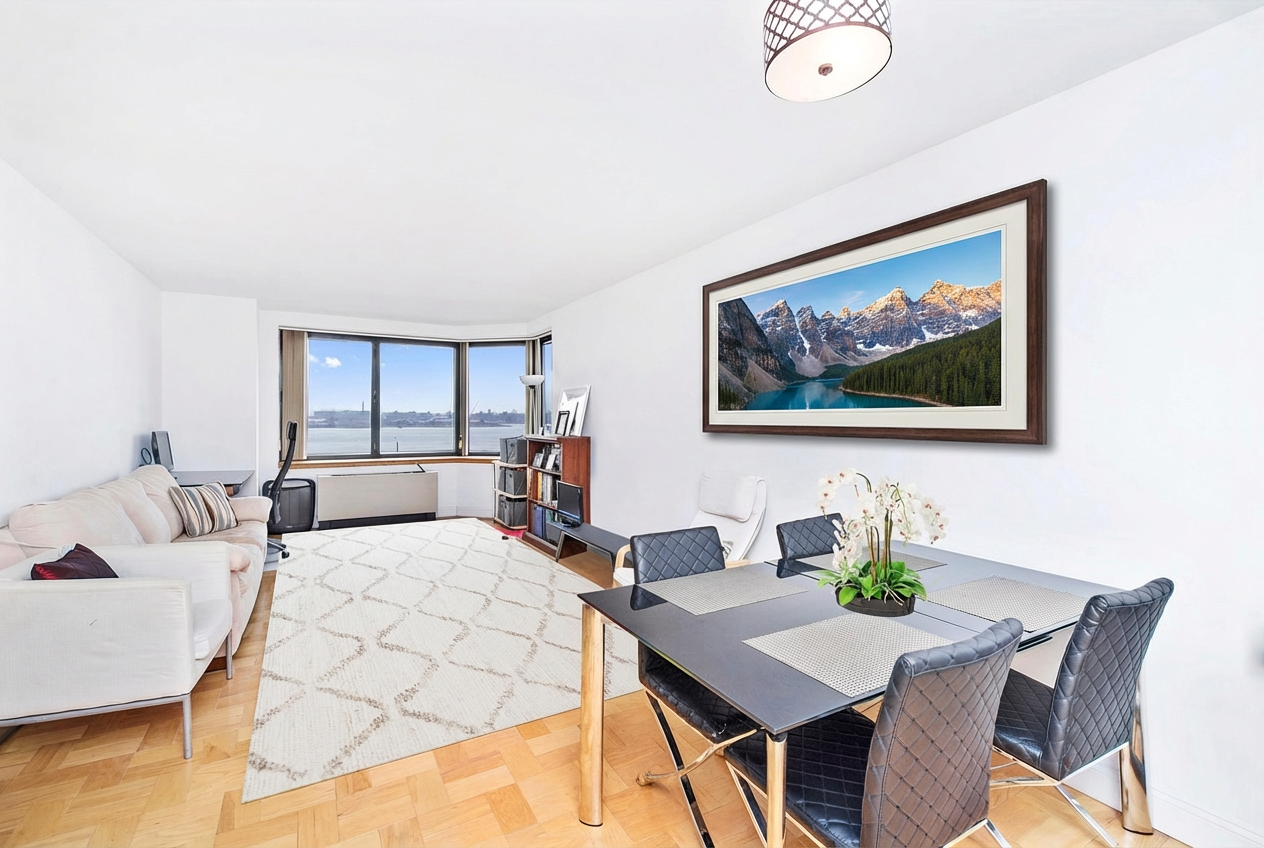
 Add a mountain picture hanging into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
Add a mountain picture hanging into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
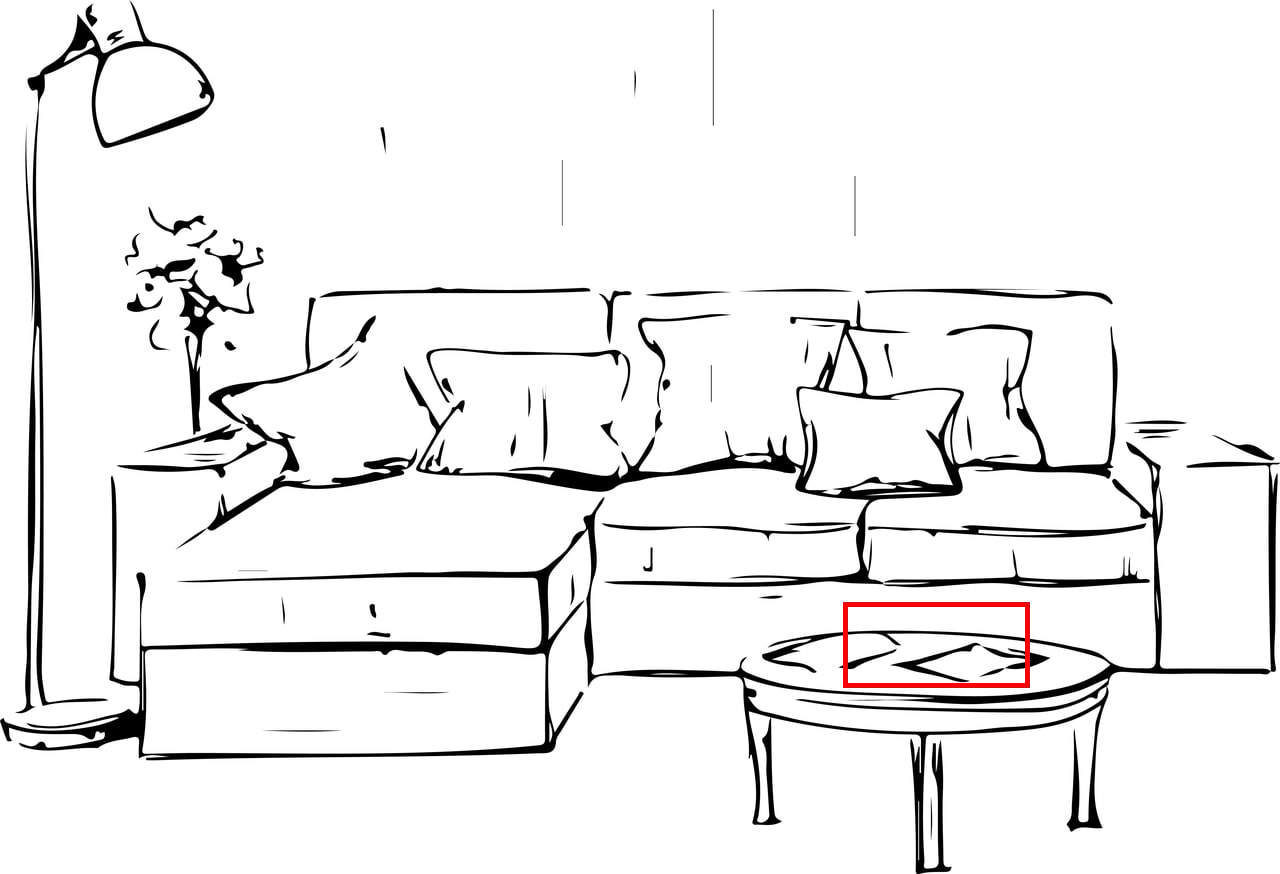
 Add some apples into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
Add some apples into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
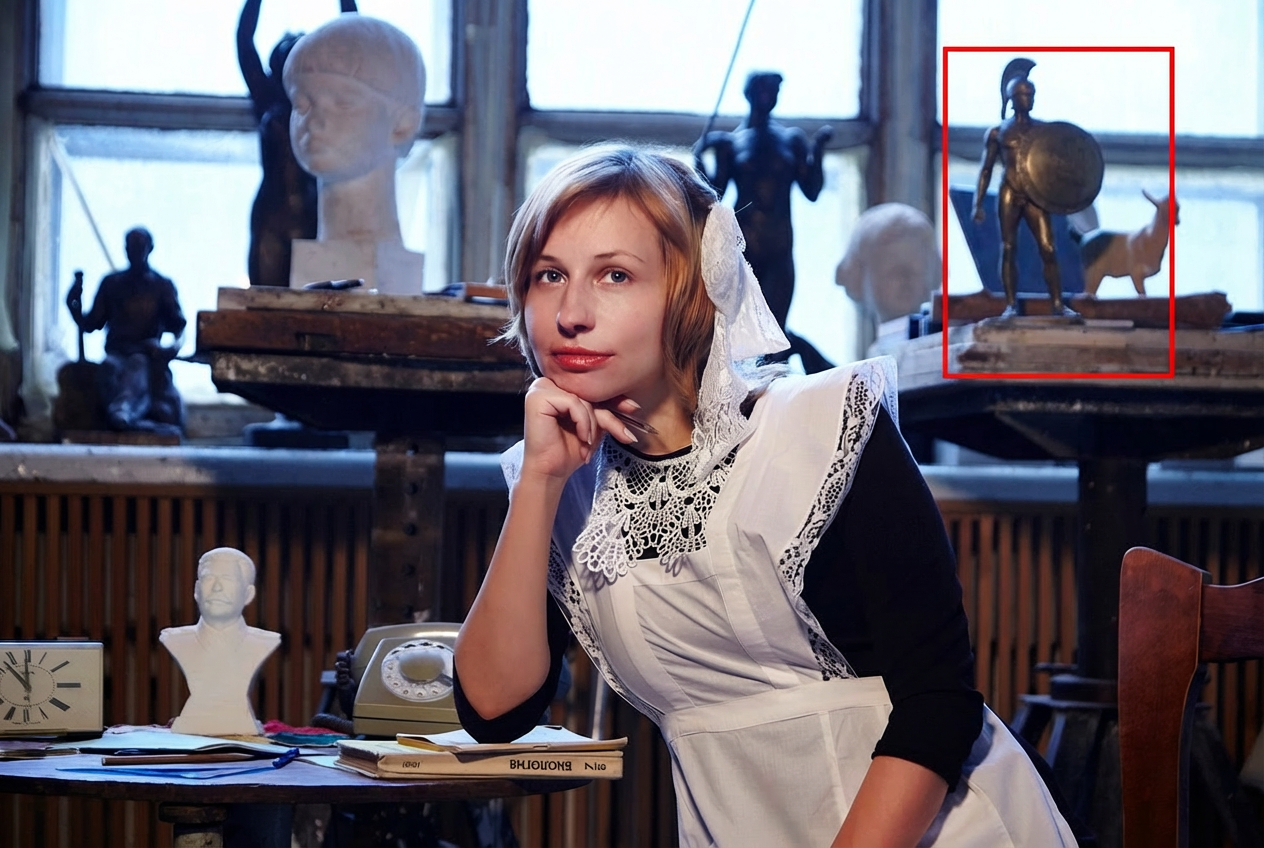
 Add a statue in the background holding a shield into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
Add a statue in the background holding a shield into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
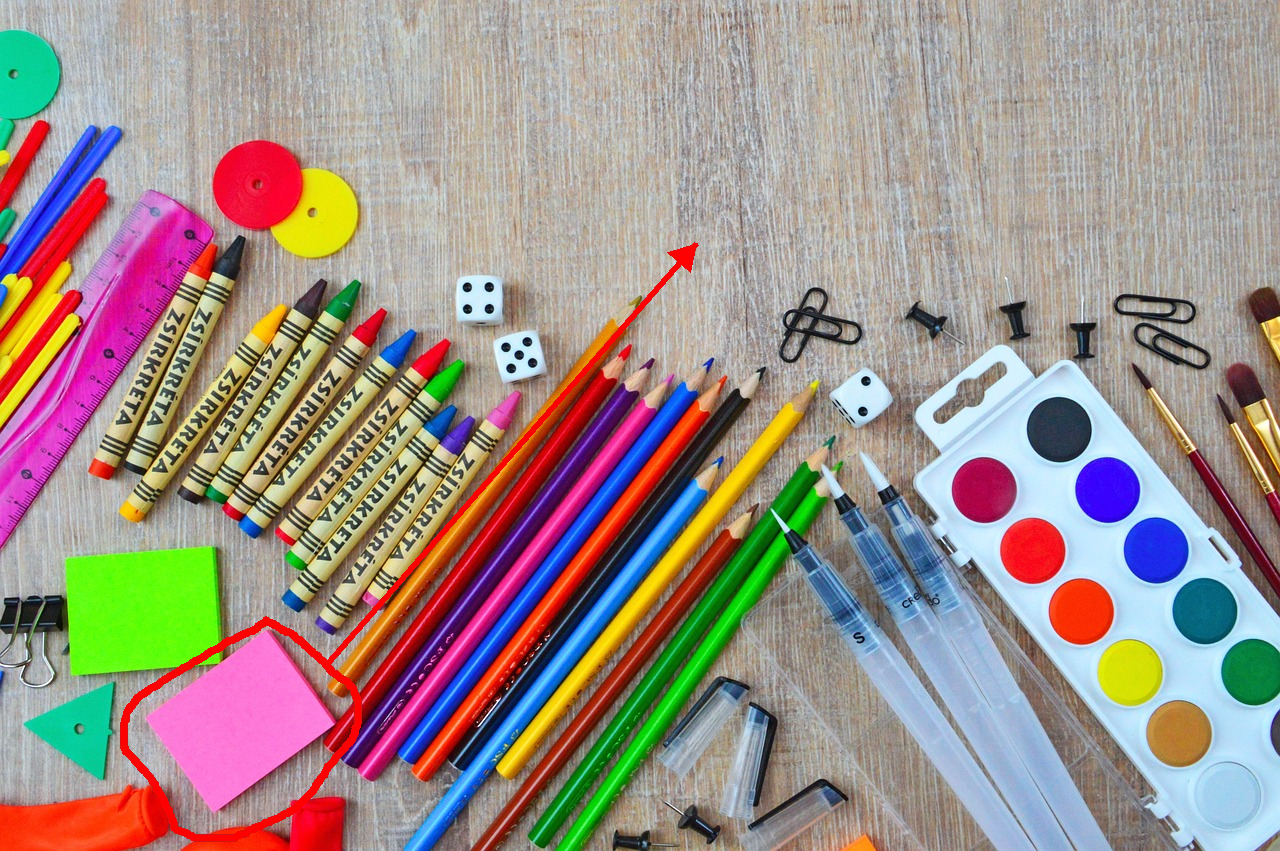
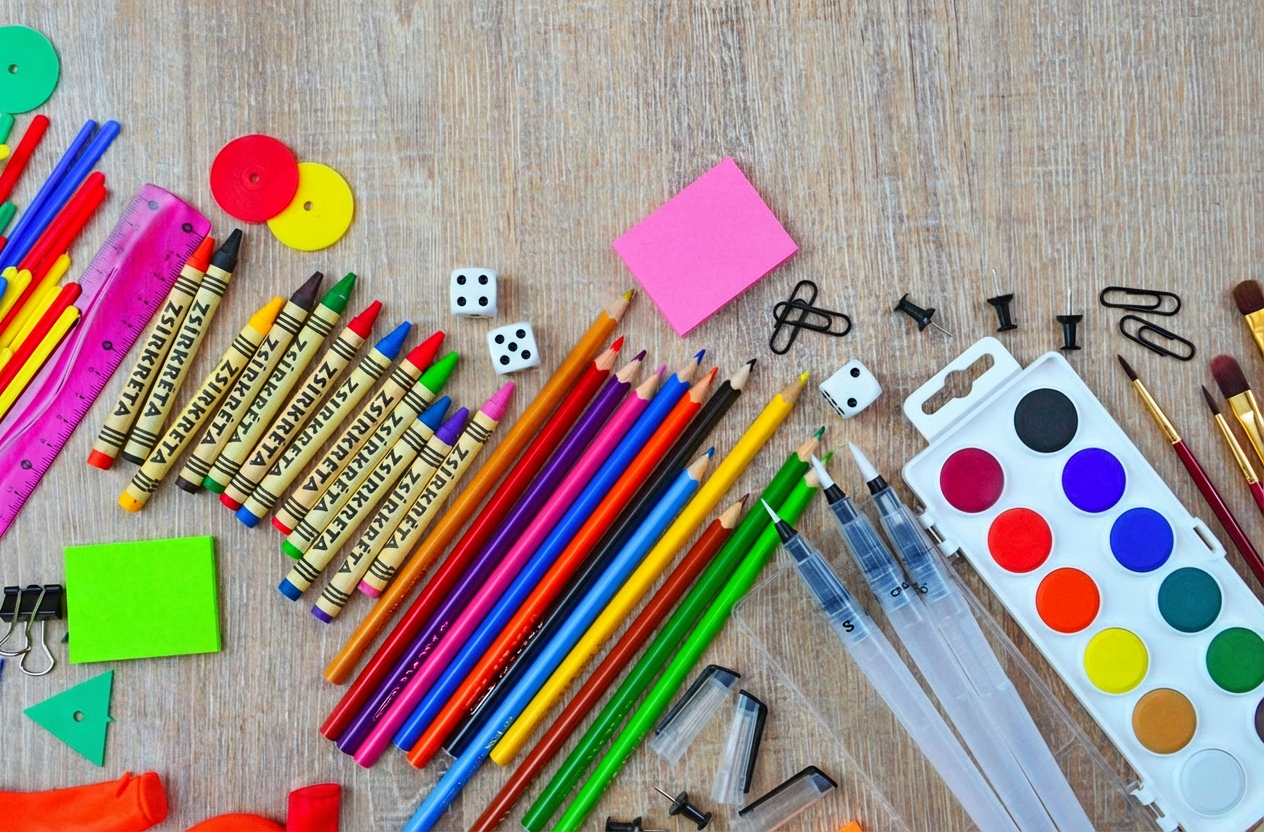
 Relocate the sticky notes highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Relocate the sticky notes highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
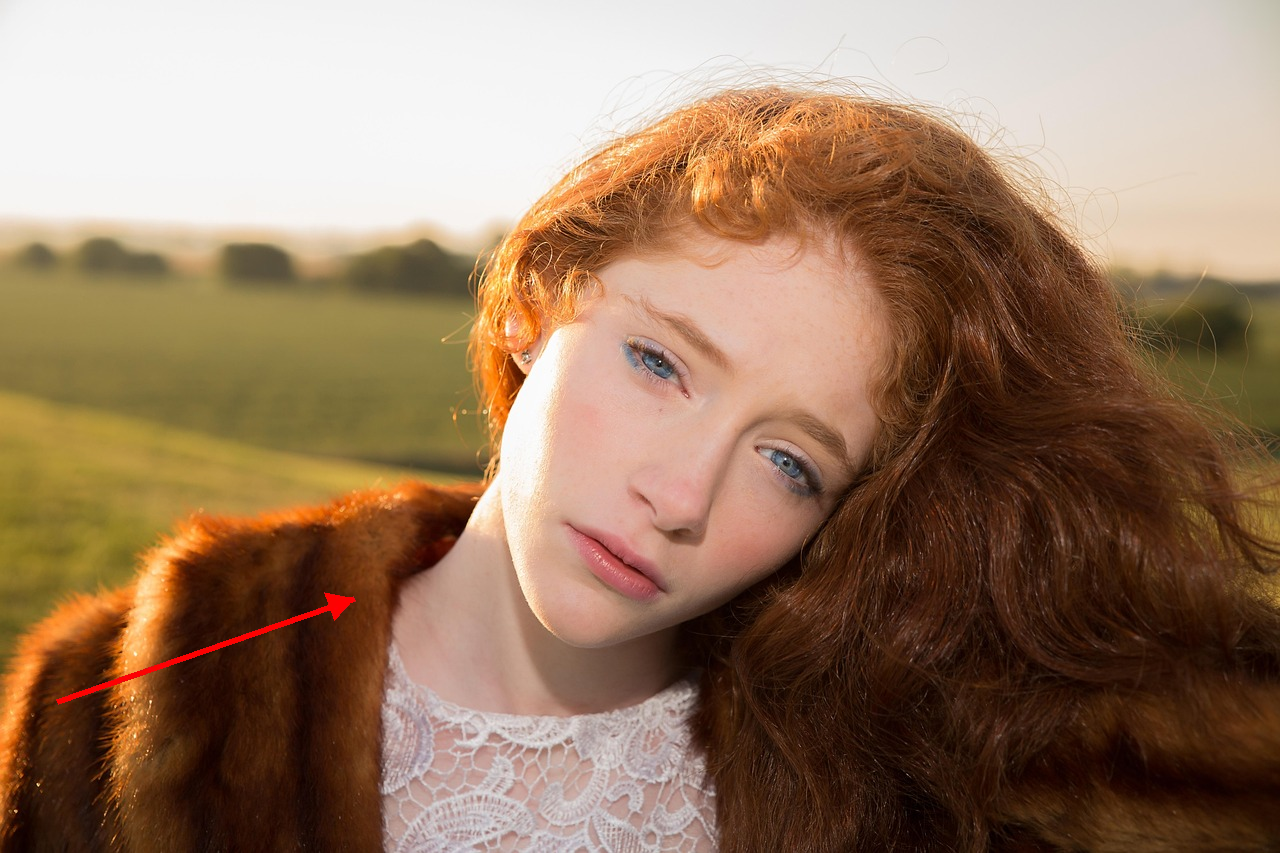
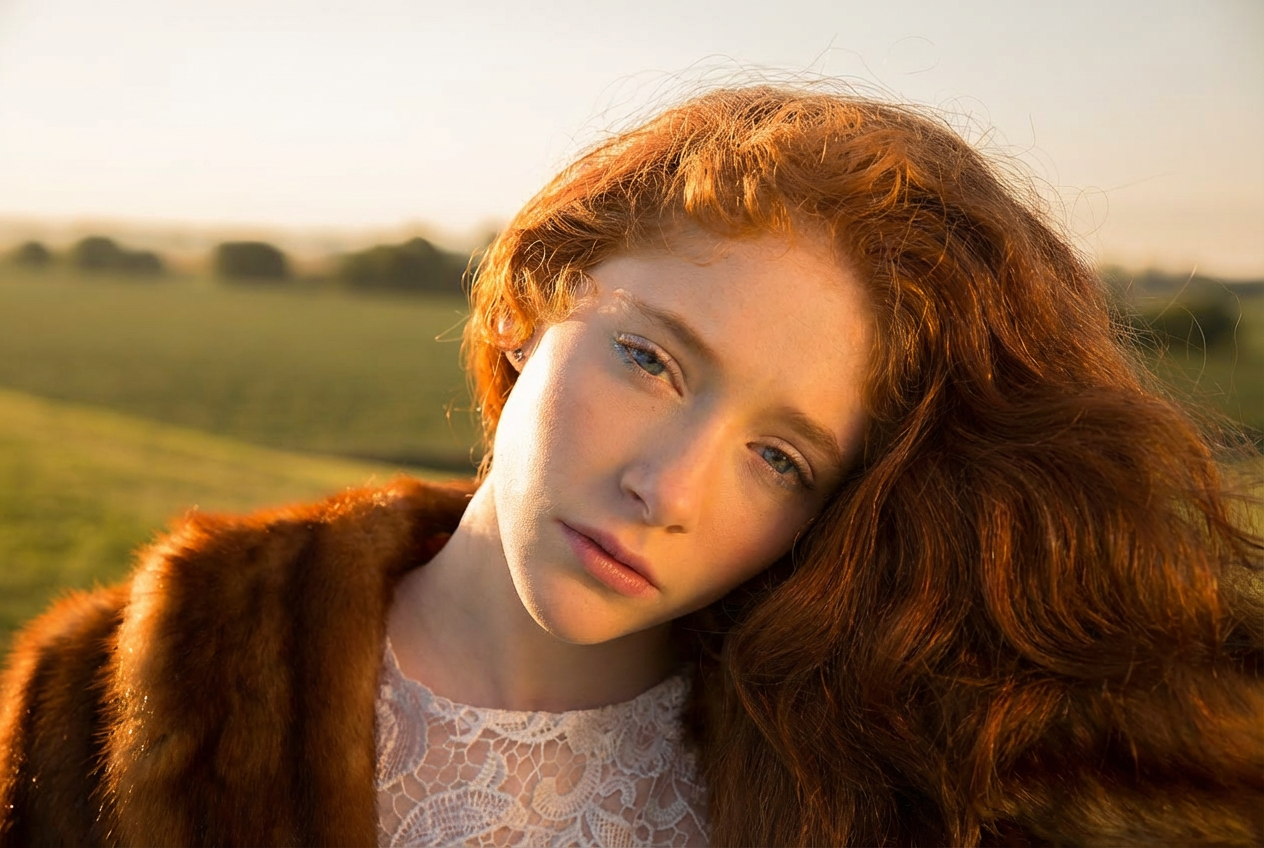
 Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
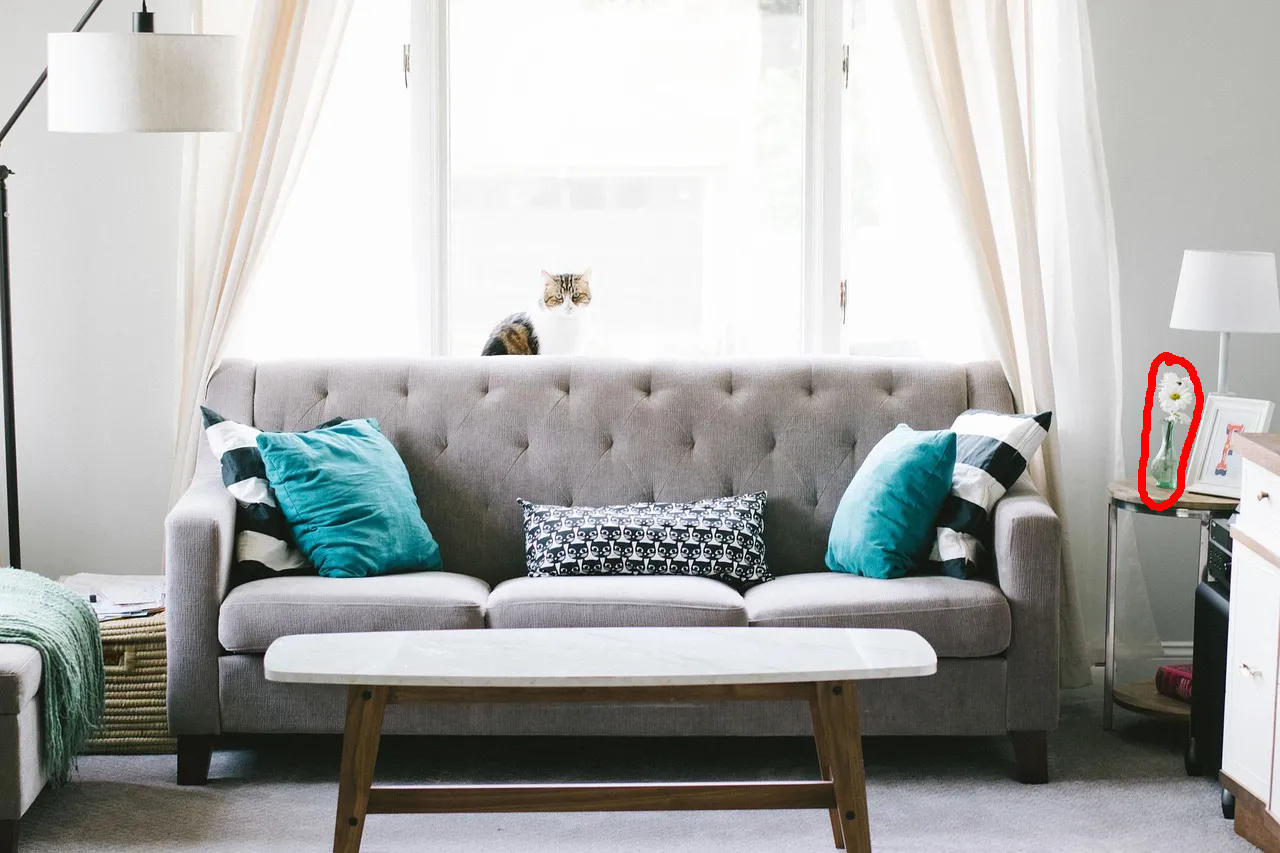
 Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
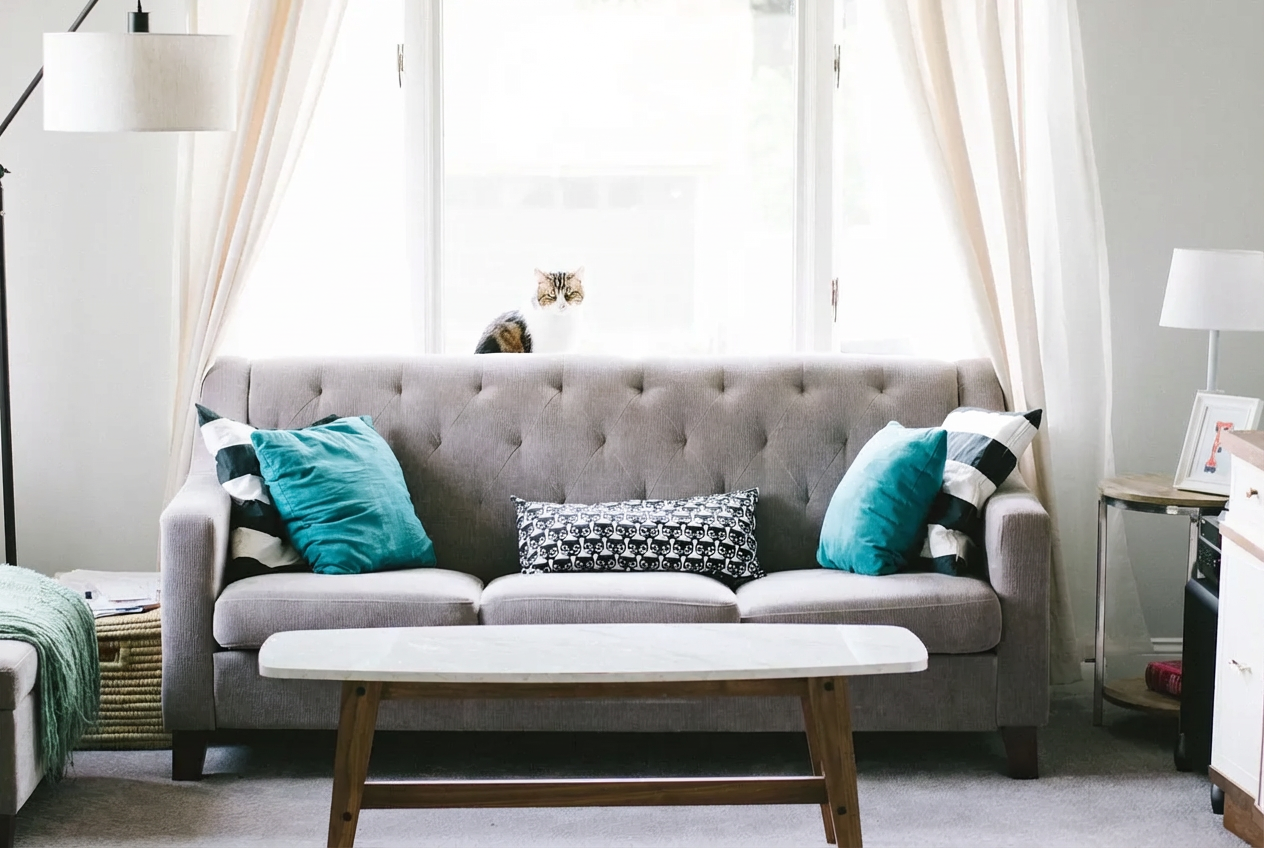
Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
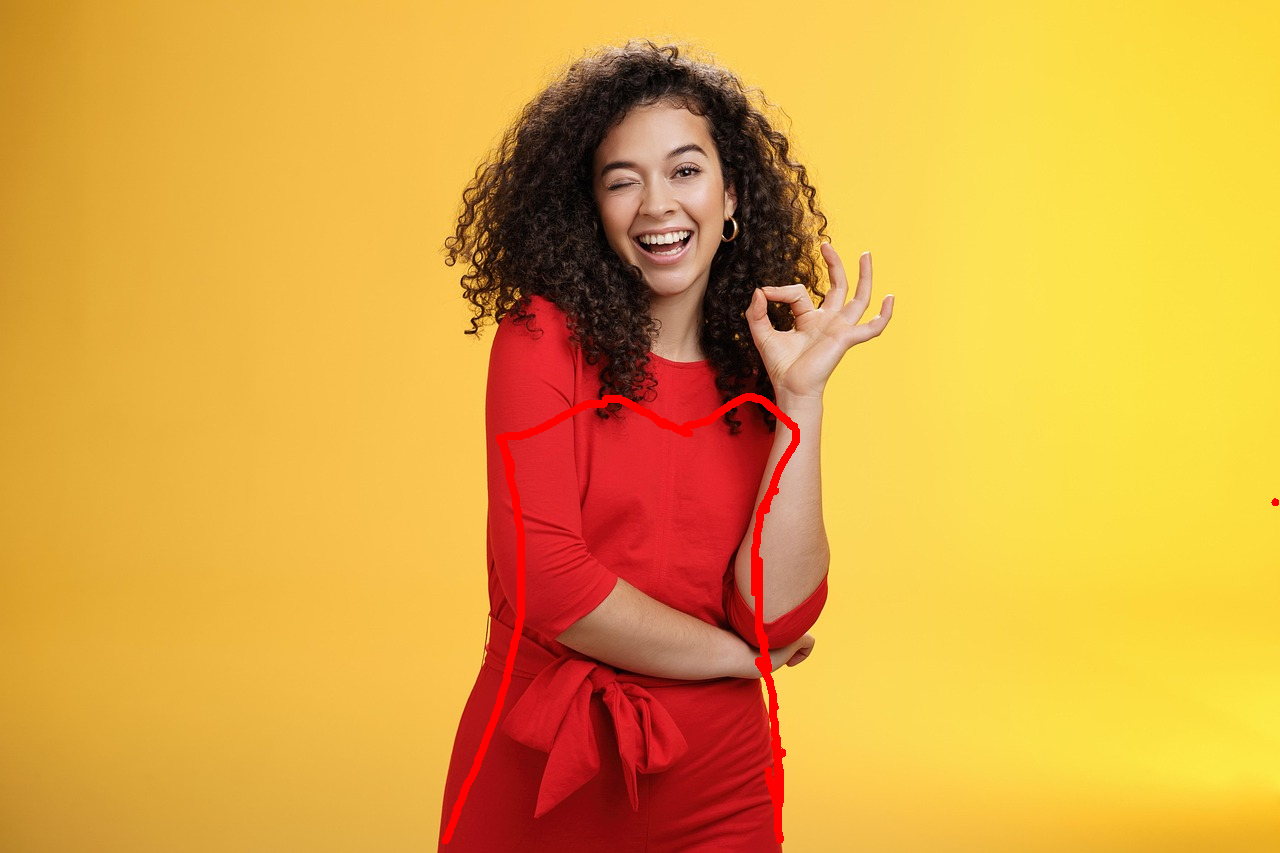
 Change this woman's clothing to a strapless top shown in the red sketch annotations in the picture.
Nano Banana Pro
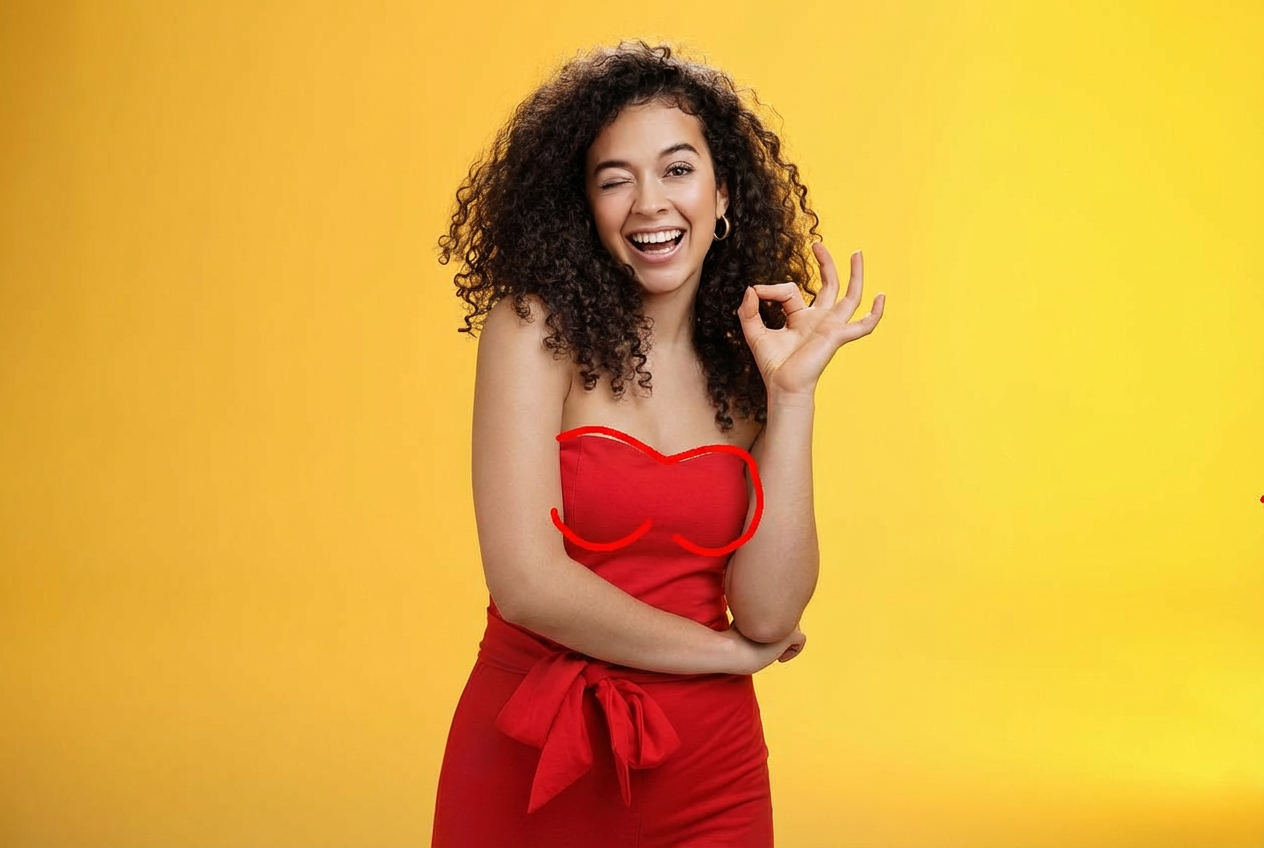
Change this woman's clothing to a strapless top shown in the red sketch annotations in the picture.
Nano Banana Pro
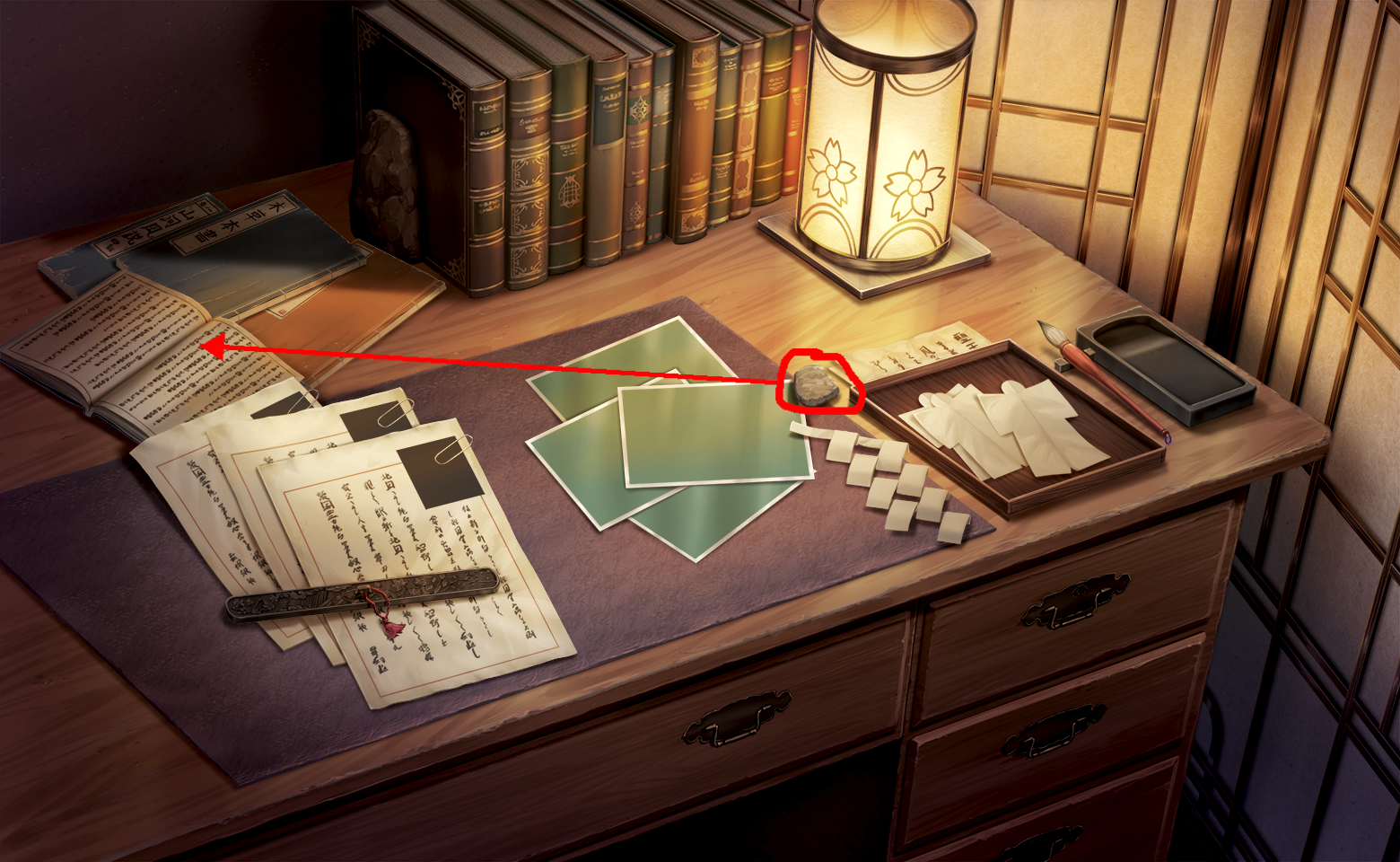

 Relocate the stone highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Relocate the stone highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
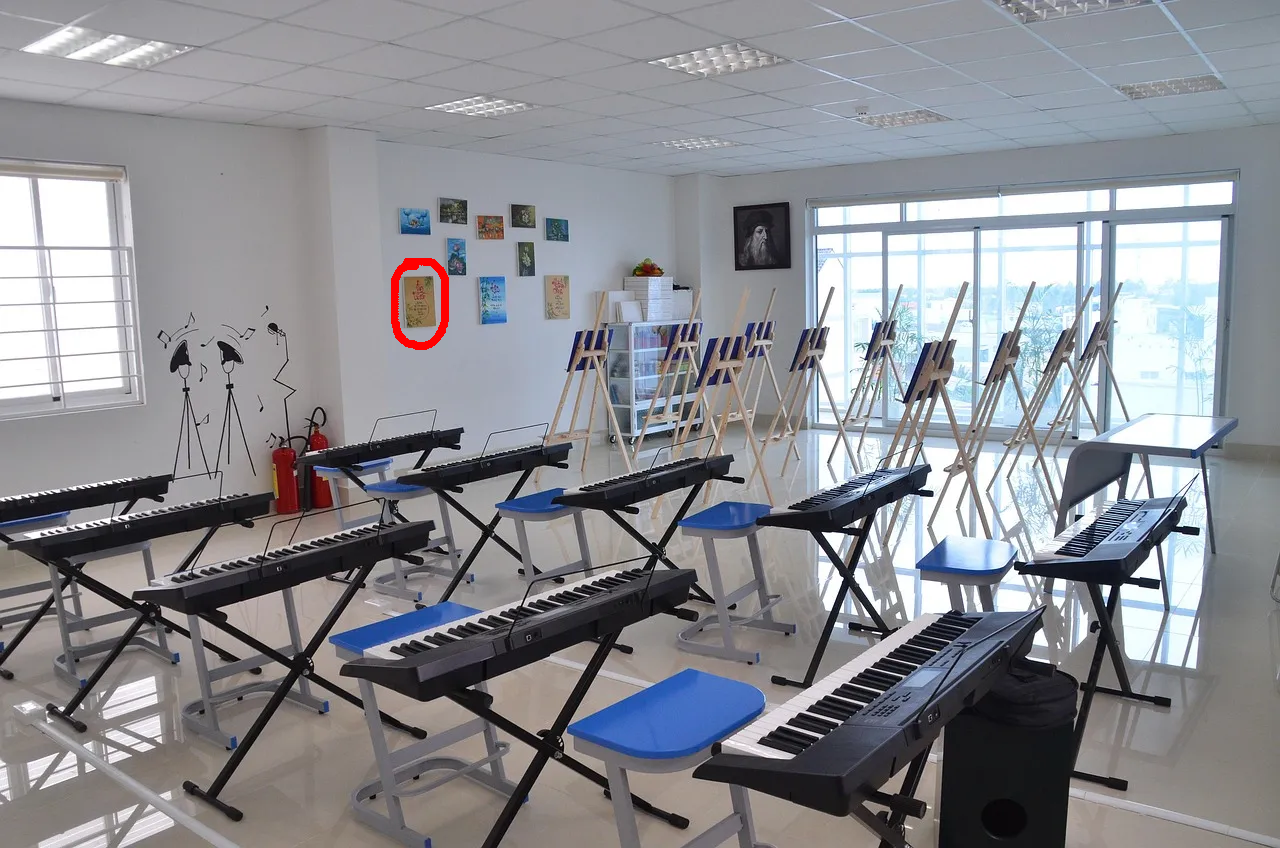
 Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
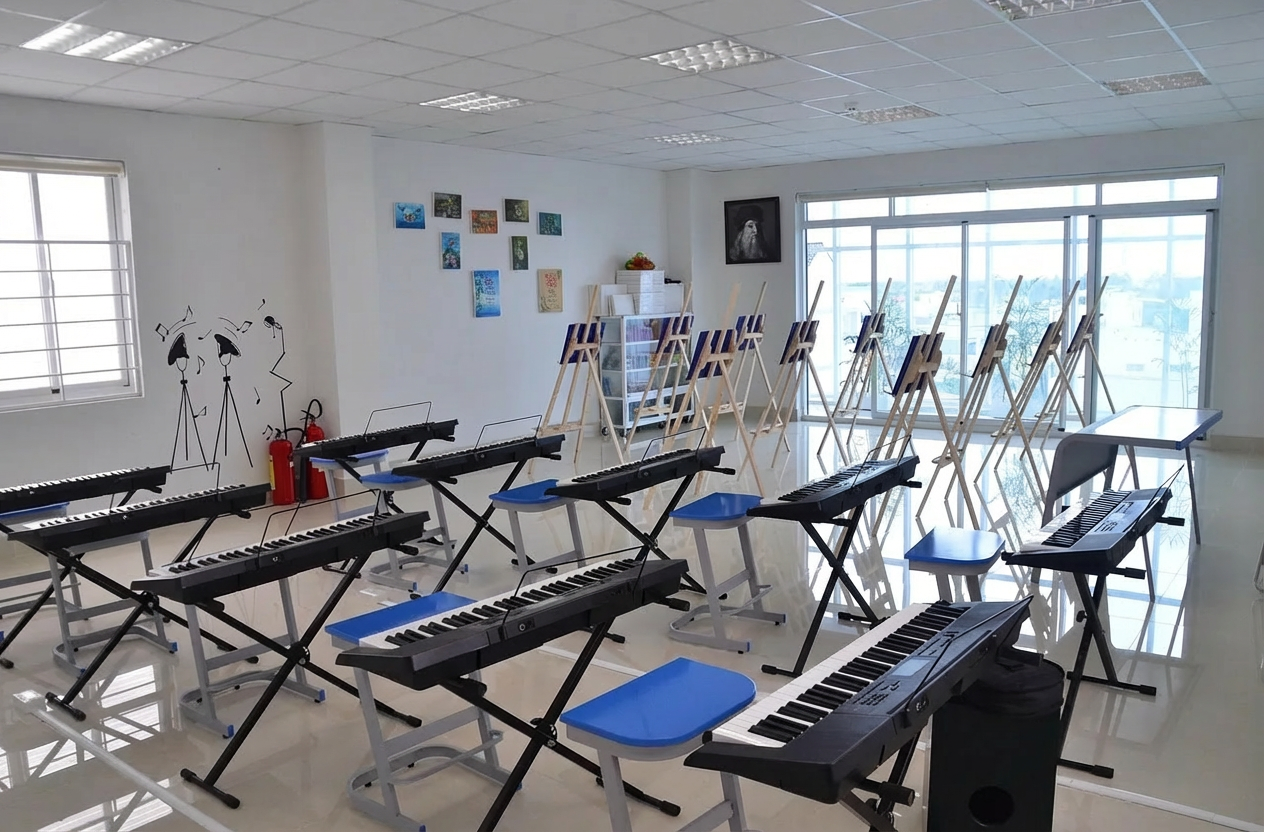
Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
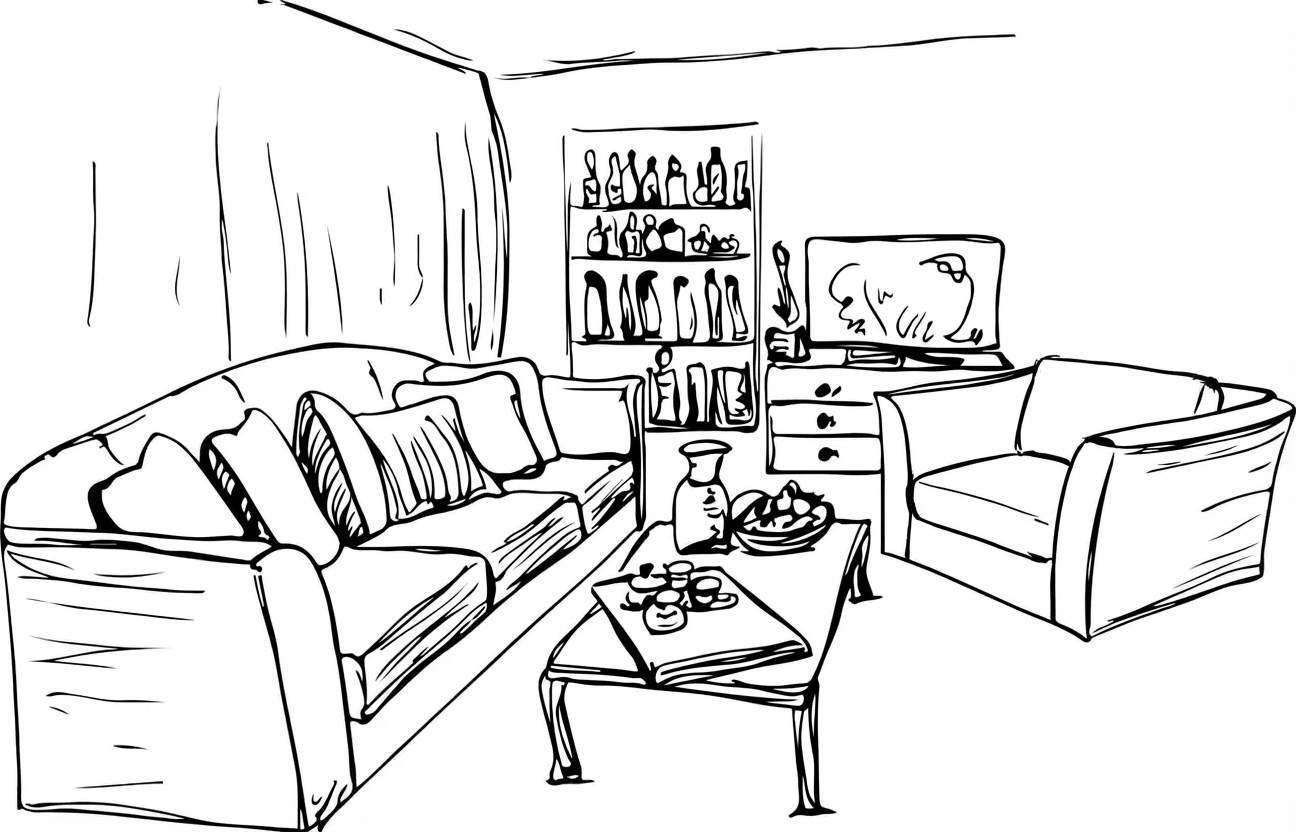
 Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
Remove all the objects in the marked region.
Nano Banana Pro
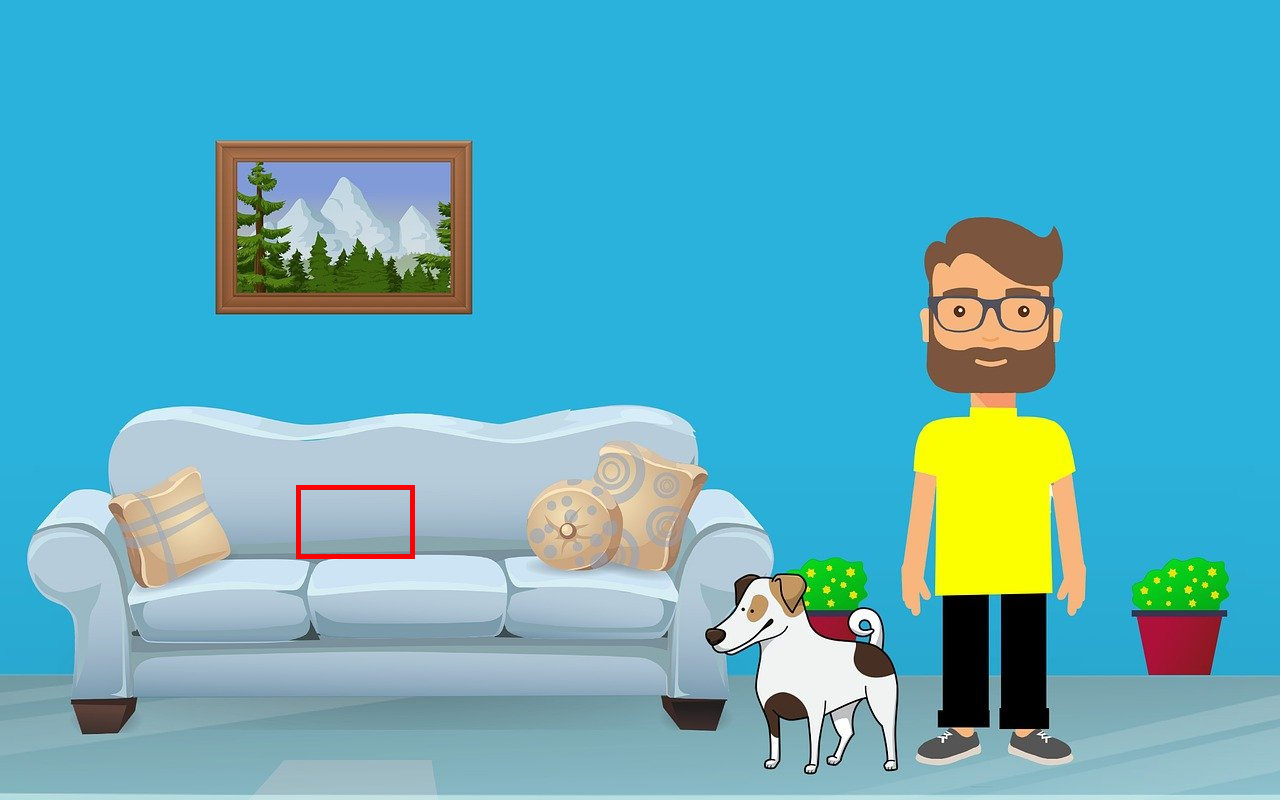
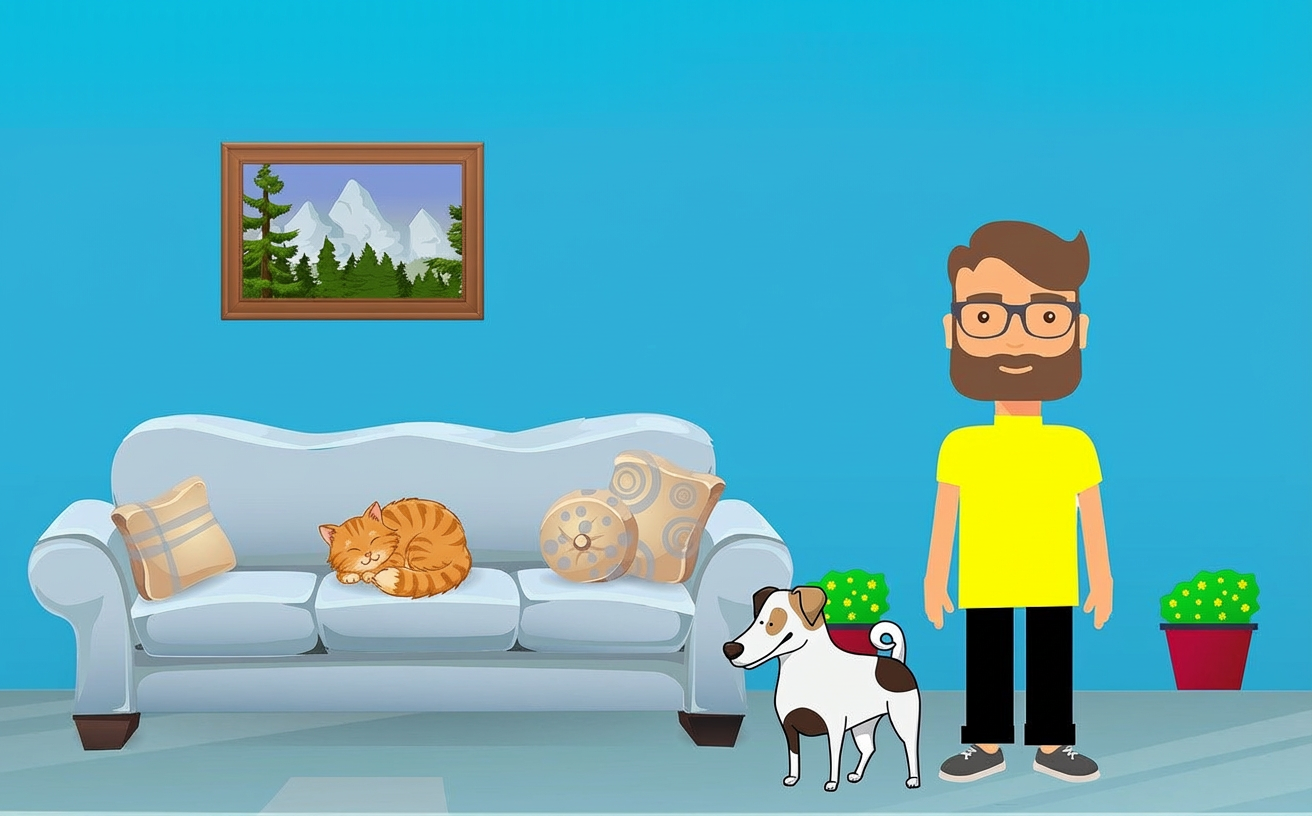
 Add a cat into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
Add a cat into the area delineated by the red bounding box.
Nano Banana Pro
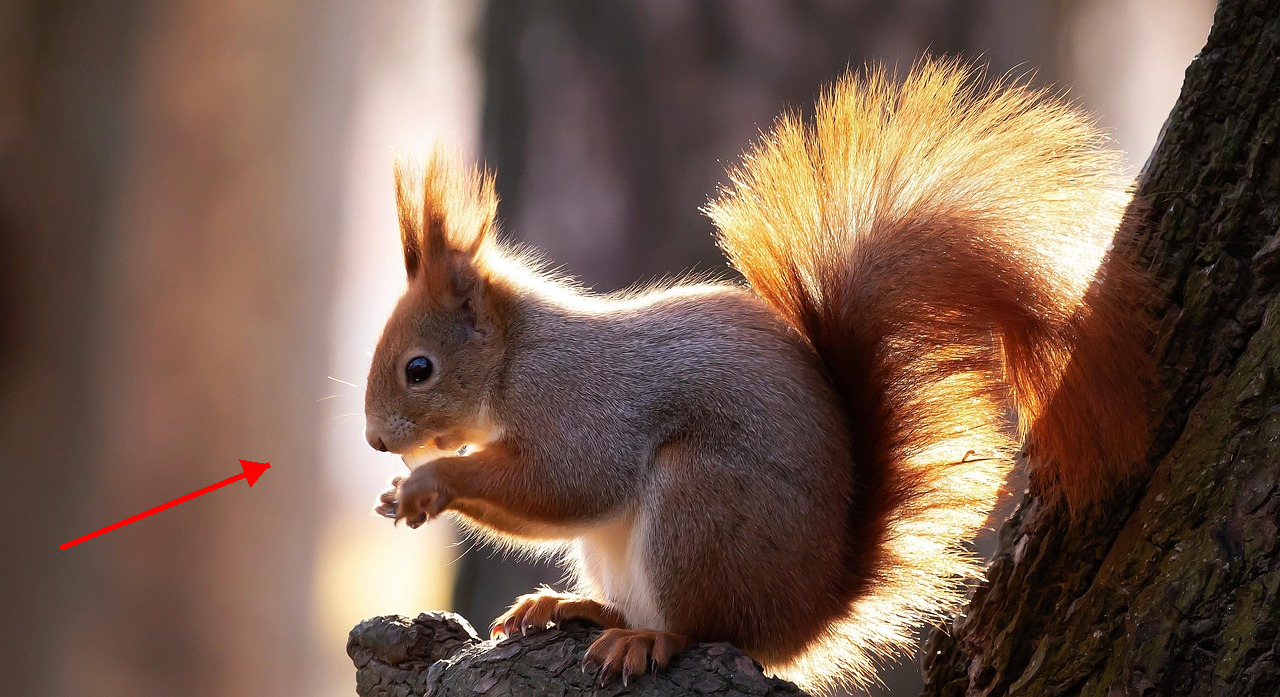
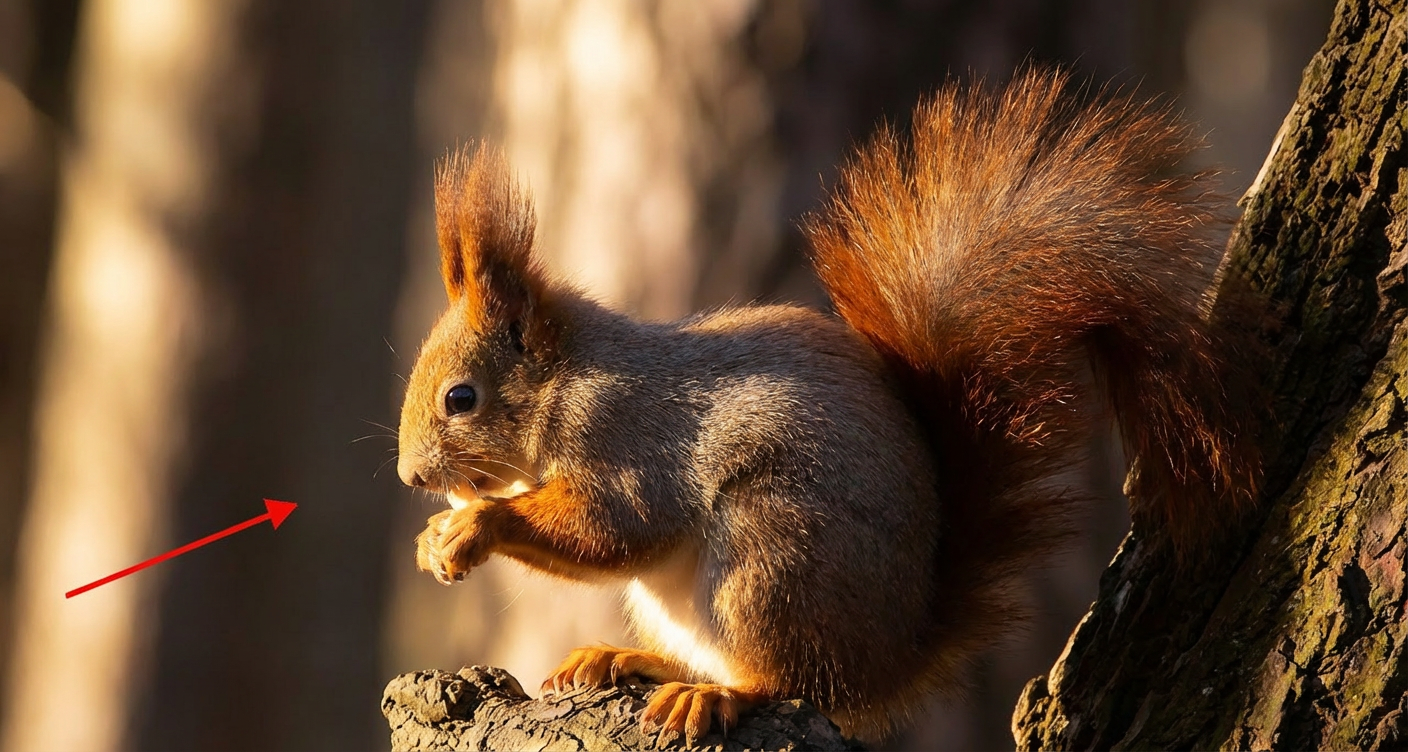
 Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
Relight the entire scene, changing the primary light source direction to align precisely with the red arrow indicator.
Nano Banana Pro
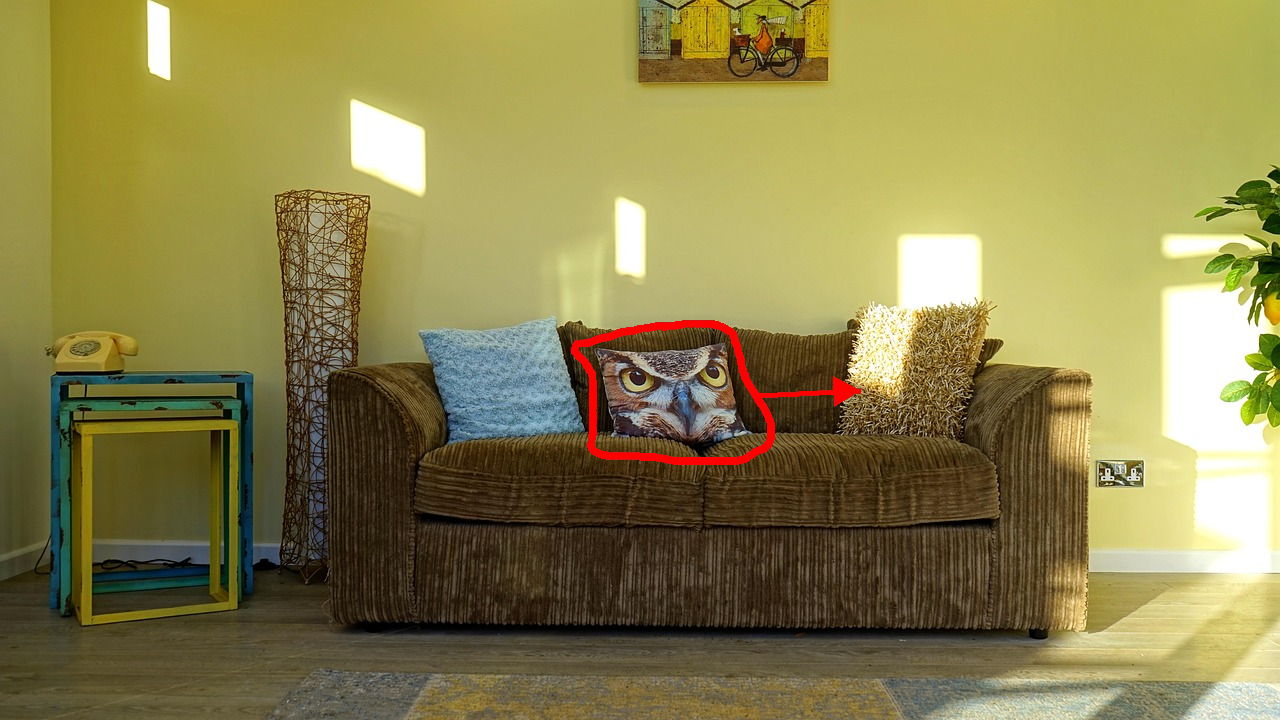
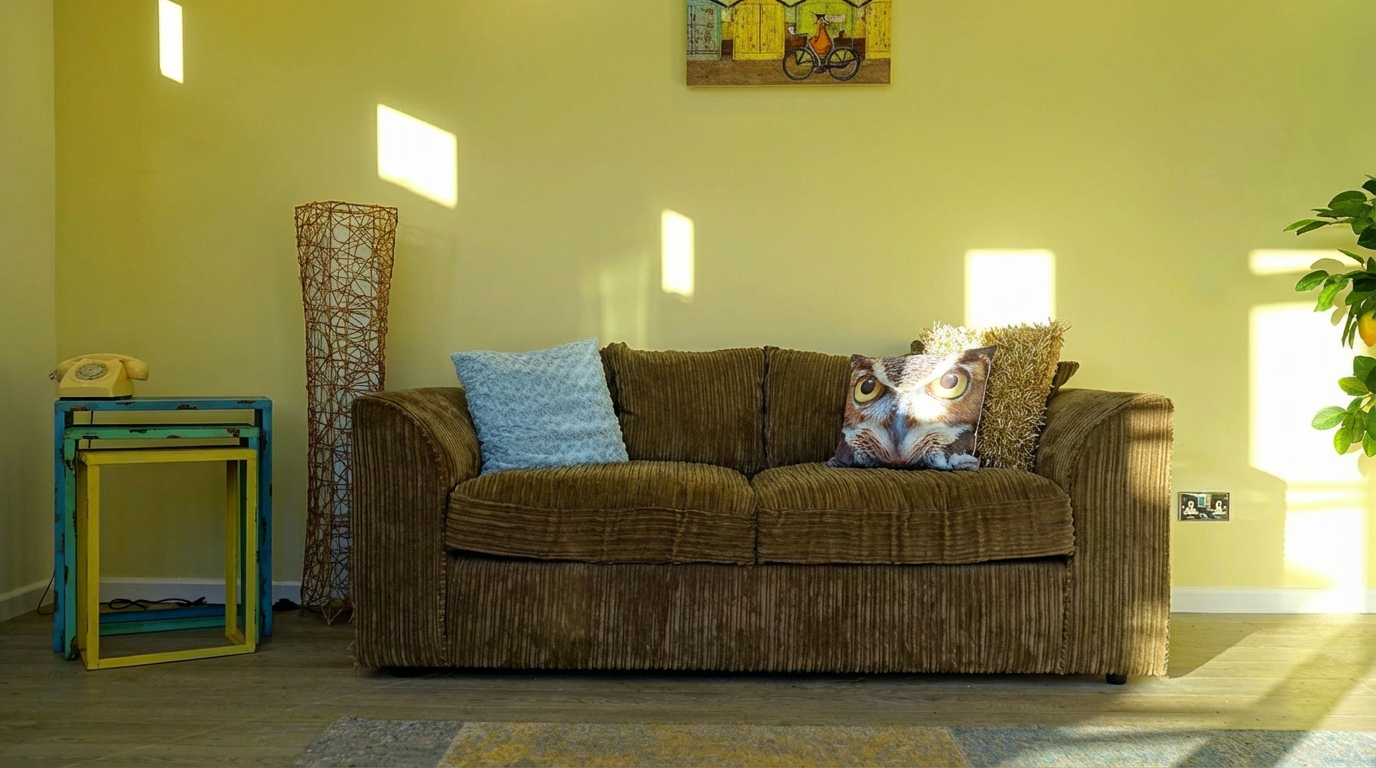
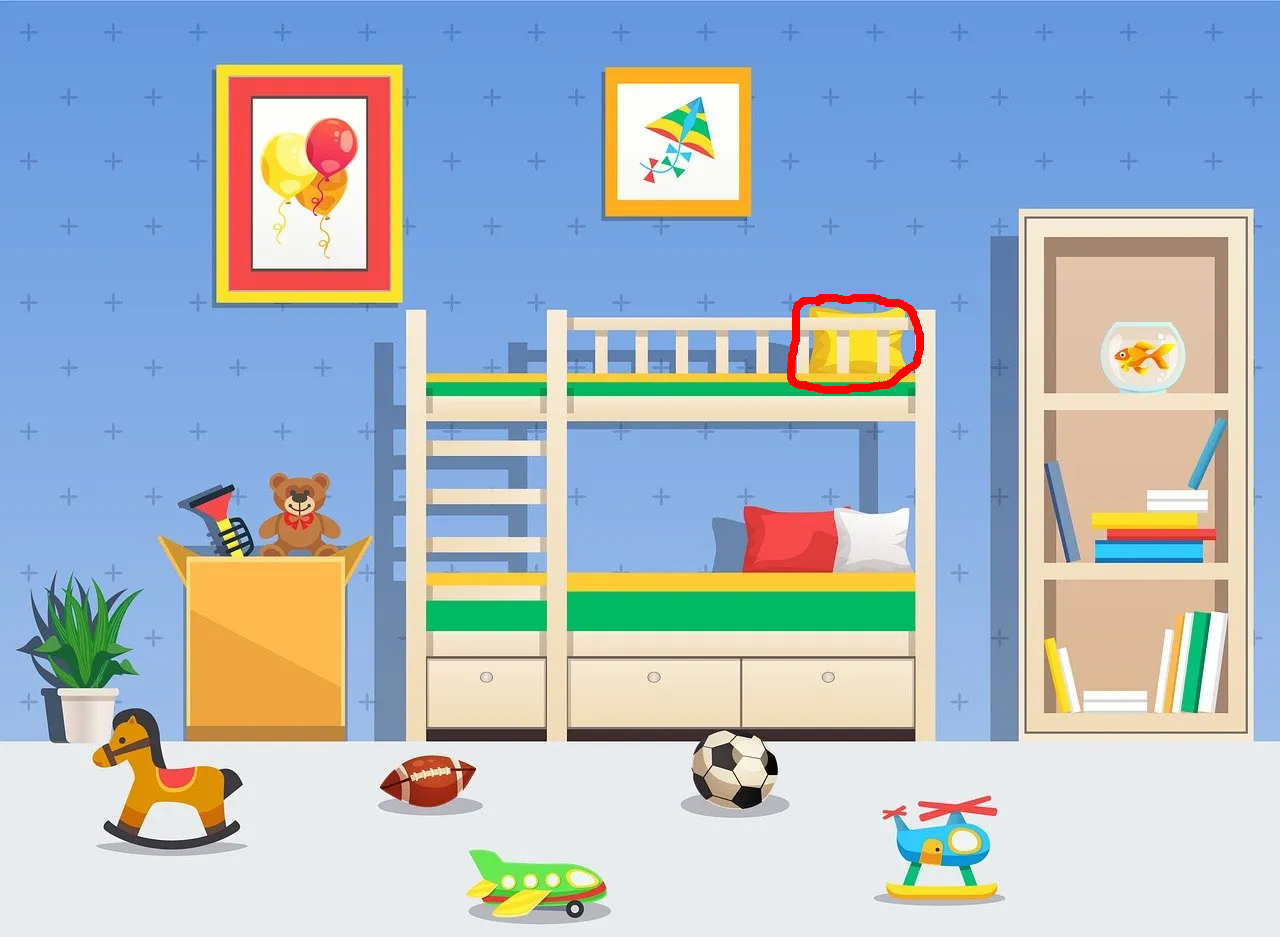
 Relocate the pillow highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
Relocate the pillow highlighted by the red outline to the spot pointed to by the red arrow.
Nano Banana Pro
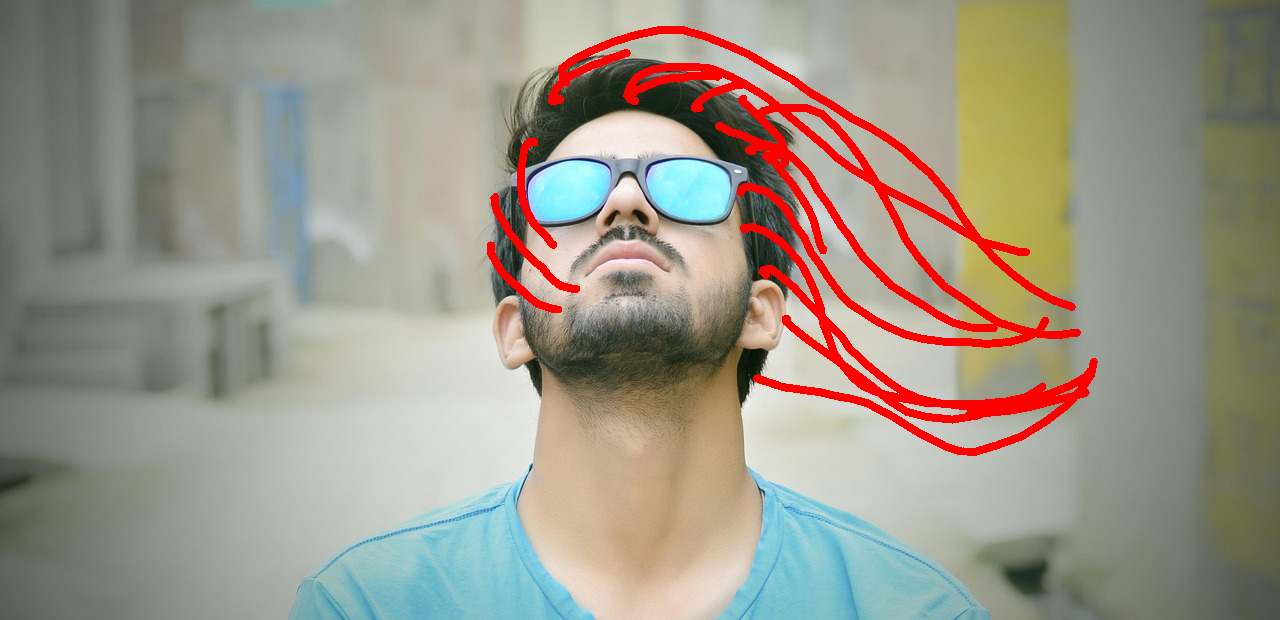
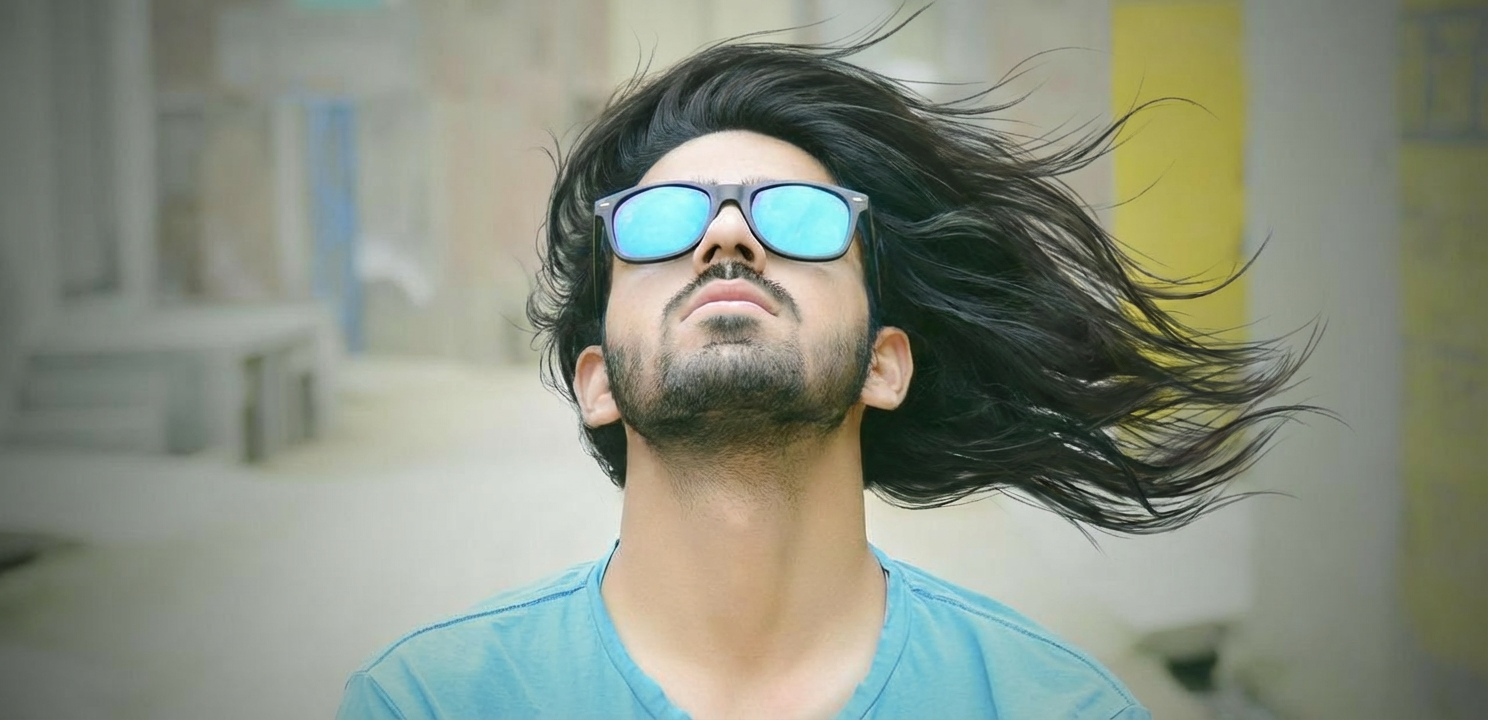
 Change this man's hairstyle to the style shown in the red sketch annotations in the picture.
Nano Banana Pro
Change this man's hairstyle to the style shown in the red sketch annotations in the picture.
Nano Banana Pro